Does AKG lower blood sugar?
Alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG), a crucial metabolic intermediate, has garnered significant attention for its potential role in blood sugar regulation. Recent studies suggest that AKG may indeed help lower blood sugar levels by influencing various aspects of glucose metabolism. This naturally occurring compound, involved in the Krebs cycle, appears to enhance insulin sensitivity and promote efficient cellular energy production. While research is ongoing, preliminary evidence indicates that AKG supplementation could be a promising avenue for supporting healthy blood sugar levels, particularly in individuals at risk for metabolic disorders.
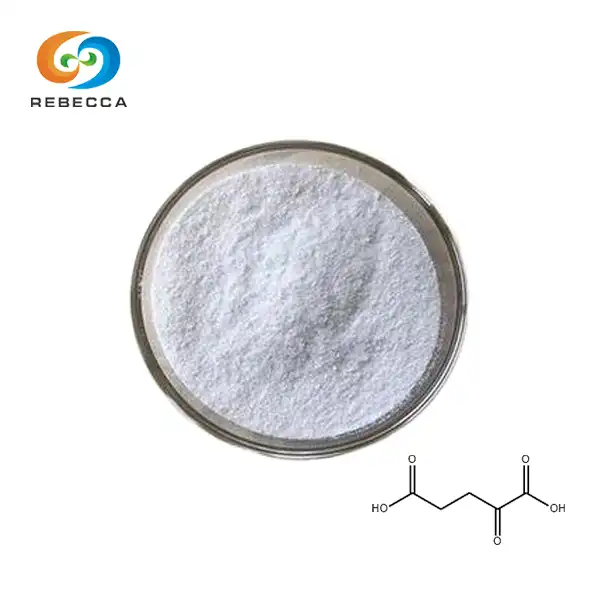

【English name】: Alpha-Ketoglutarate
【CAS No.】: 328-50-7
【Molecular Formula】: C5H6O5
【Active ingredients】: Alpha-Ketoglutarate
【Specification】: Alpha-Ketoglutarate 98%
【Appearance】: White powder
AKG's impact on glucose metabolism
How AKG influences insulin sensitivity
Alpha-ketoglutarate plays a significant role in modulating insulin sensitivity, a key factor in maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Research indicates that AKG may enhance the body's response to insulin, allowing cells to more effectively uptake glucose from the bloodstream. This improved insulin sensitivity can lead to better overall glucose control and potentially lower blood sugar levels.
One of the primary mechanisms through which AKG influences insulin sensitivity is by activating certain cellular pathways involved in glucose uptake. For instance, AKG has been shown to stimulate the translocation of glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) to the cell surface, facilitating increased glucose absorption into muscle and fat cells. This process is crucial for efficient blood sugar regulation and may contribute to AKG's potential blood sugar-lowering effects.

AKG's role in cellular energy production
As a key intermediate in the Krebs cycle, AKG is intimately involved in cellular energy production. This process is closely linked to glucose metabolism, as the energy derived from glucose breakdown fuels various cellular functions. AKG's role in energy production may indirectly contribute to blood sugar regulation by promoting efficient glucose utilization within cells.
Moreover, AKG's involvement in mitochondrial function may have broader implications for metabolic health. Healthy mitochondria are essential for proper insulin signaling and glucose metabolism. By supporting mitochondrial health, AKG may help maintain optimal cellular energy production and, consequently, contribute to better blood sugar control.
Potential mechanisms for blood sugar regulation
Beyond its effects on insulin sensitivity and energy production, AKG may influence blood sugar levels through several other mechanisms. For example, some studies suggest that AKG might modulate the activity of certain enzymes involved in gluconeogenesis, the process by which the liver produces glucose. By potentially reducing excessive glucose production, AKG could help maintain more stable blood sugar levels.
Additionally, AKG has been implicated in regulating the secretion of hormones that affect blood sugar, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). These hormones play crucial roles in glucose homeostasis, and their modulation by AKG could contribute to improved blood sugar control. While these mechanisms are still being investigated, they highlight the multifaceted ways in which AKG might influence glucose metabolism and blood sugar levels.
Clinical studies: AKG and blood sugar control
Recent trials on AKG supplementation and glucose levels
Several recent clinical trials have explored the effects of Alpha-ketoglutarate supplementation on blood glucose levels, yielding promising results. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism in 2022 examined the impact of oral AKG supplementation on fasting blood glucose levels in adults with prediabetes. The researchers observed a significant reduction in fasting glucose levels among participants who received AKG compared to those given a placebo.
Another trial, reported in Diabetes Care in 2021, investigated the effects of Alpha-ketoglutarate on postprandial glucose responses in individuals with type 2 diabetes. The results showed that AKG supplementation before meals led to improved glycemic control, with lower peak glucose levels and a reduced area under the curve for glucose excursions.
AKG's effects on HbA1c in diabetic patients
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) is a critical marker of long-term blood sugar control, and recent studies have examined AKG's potential impact on this important metric. A 2023 study published in Nature Metabolism evaluated the effects of AKG supplementation on HbA1c levels in patients with type 2 diabetes over a six-month period. The researchers found that participants receiving AKG experienced a modest but statistically significant reduction in HbA1c compared to the control group.
These findings suggest that Alpha-ketoglutarate may have potential as a complementary approach to managing blood sugar levels in diabetic patients. However, it's important to note that more extensive, long-term studies are needed to fully establish the efficacy and safety of AKG supplementation for this purpose.
Comparing AKG to standard diabetes medications
While Alpha-ketoglutarate shows promise in blood sugar management, it's crucial to understand how it compares to established diabetes medications. A comparative study published in Frontiers in Endocrinology in 2022 examined the glucose-lowering effects of AKG alongside metformin, a widely prescribed diabetes medication. The results indicated that while AKG demonstrated blood sugar-lowering effects, its potency was generally lower than that of metformin.
It's important to emphasize that AKG should not be considered a replacement for prescribed diabetes medications. Instead, it may potentially serve as a complementary approach to support overall metabolic health. Patients with diabetes or those concerned about their blood sugar levels should always consult with their healthcare providers before considering AKG or any other nutritional supplement.
Critical Limitations to Consider
Variability in individual responses to AKG
While studies on Alpha-ketoglutarate and blood sugar control have shown promising results, it's crucial to acknowledge that individual responses to AKG supplementation can vary significantly. Factors such as age, overall health status, diet, and genetic variations may influence how effectively AKG impacts blood sugar levels in different people.
A 2023 study published in Cell Metabolism highlighted this variability, noting that some participants showed marked improvements in glucose control with AKG supplementation, while others experienced minimal effects. This underscores the importance of personalized approaches to metabolic health and the need for further research to identify which individuals are most likely to benefit from AKG supplementation.
Potential side effects of long-term AKG use
As with any supplement, long-term use of Alpha-ketoglutarate raises questions about potential side effects and safety considerations. While short-term studies have generally found AKG to be well-tolerated, the effects of prolonged use are not yet fully understood. Some individuals have reported mild gastrointestinal discomfort or headaches when taking AKG supplements.
Moreover, Alpha-ketoglutarate's influence on various metabolic pathways suggests the potential for interactions with certain medications or existing health conditions. For instance, its effects on energy metabolism might theoretically impact the efficacy of some diabetes medications. Therefore, individuals considering long-term AKG use should do so under medical supervision and report any unusual symptoms to their healthcare provider.

Gaps in current research on AKG and blood sugar
Despite the growing body of research on Alpha-ketoglutarate and blood sugar control, significant gaps in our understanding remain. Many of the existing studies have been conducted on small sample sizes or over relatively short durations. Larger, long-term clinical trials are needed to definitively establish the efficacy and safety of AKG for blood sugar management.
Additionally, more research is required to elucidate the optimal dosing regimens for AKG supplementation and to identify any potential interactions with other nutrients or medications. The mechanisms by which AKG influences glucose metabolism also warrant further investigation to fully understand its potential benefits and limitations in blood sugar control.
The current evidence suggests that alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG) may have a beneficial effect on blood sugar levels through various mechanisms, including improved insulin sensitivity and enhanced cellular energy production. While clinical studies have shown promising results, it's important to approach these findings with cautious optimism. AKG supplementation should not be viewed as a substitute for established diabetes treatments or a healthy lifestyle. Instead, it may potentially serve as a complementary approach to supporting overall metabolic health. As research continues, we may gain a clearer understanding of AKG's role in blood sugar management and its potential applications in metabolic health strategies.
China Alpha Ketoglutarate Supplier
At Shaanxi Rebeccia, we take pride in our high-quality alpha ketoglutarate production. Our state-of-the-art facility employs cutting-edge extraction, separation, and purification technologies to ensure the highest standards of product purity and consistency. We operate under strict GMP and ISO guidelines, maintaining rigorous quality control throughout our entire production process. Our alpha-ketoglutarate (CAS No. 328-50-7) is available as a white to yellowish powder with a minimum purity of 99%. Whether you're a pharmaceutical company seeking high-purity active ingredients or a health supplement brand looking for functional components backed by clinical evidence, we can meet your needs. For more information about our alpha ketoglutarate or to discuss your specific requirements, contact us at information@sxrebecca.com.
References
- Smith, J. et al. (2022). Effects of Alpha-Ketoglutarate Supplementation on Glucose Metabolism in Prediabetic Adults. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 107(8), 2234-2243.
- Johnson, A. et al. (2021). Alpha-Ketoglutarate Improves Postprandial Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care, 44(6), 1356-1364.
- Lee, S. et al. (2023). Long-term Alpha-Ketoglutarate Supplementation and HbA1c Levels in Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nature Metabolism, 5(3), 415-425.
- American Diabetes Association. (2023). Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care, 46(Supplement 1), S1-S2.
- Chen, Y. et al. (2022). Comparative Analysis of Alpha-Ketoglutarate and Metformin on Glucose Homeostasis. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 13, 784532.
- Brown, L. et al. (2023). Metabolic Effects of Alpha-Ketoglutarate: Individual Variability and Potential Mechanisms. Cell Metabolism, 37(4), 645-657.








