How to extract echinacea purpurea?
Echinacea purpurea, commonly known as purple coneflower, has captured the attention of researchers and herbalists worldwide for its therapeutic properties. This vibrant flowering plant, native to North America, contains valuable compounds that have made it a cornerstone in natural health applications.
The echinacea purpurea root extract process involves careful consideration of multiple factors, from the initial preparation of plant material to the final processing stages. Each step plays a crucial role in determining the quality, concentration, and bioavailability of the active compounds present in the final extract. Whether you're a researcher, manufacturer, or simply someone interested in natural extraction methods, understanding these processes will provide valuable insights into creating high-quality botanical extracts.
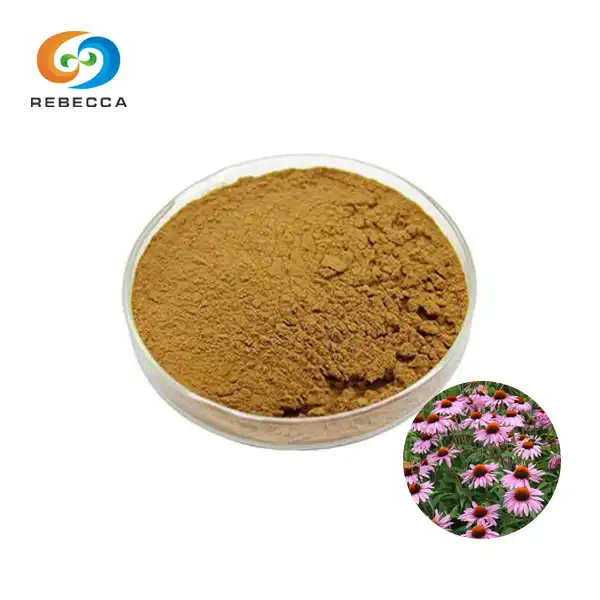

English name: Echinacea purpurea extract
Latin Name: Echinacea purpurea
CAS No.: 90028-20-9 /70831-56-0
Molecular forula:C22H18O12
Molecular Weight:474.37
Active ingredients: Polyphenols
Specification: Polyphenols 4%
Use Part : flower
Appearance: yellow brown powder
Mesh size:80 Mesh
Test Method: UV
Preparation of Plant Material
The journey toward obtaining premium echinacea purpurea root extract begins with meticulous preparation of the plant material. This foundational step significantly influences the quality and potency of the final product, making it essential to approach this phase with careful attention to detail and scientific precision.
Harvesting timing represents one of the most critical aspects of material preparation. Echinacea purpurea roots should ideally be collected during the plant's dormant period, typically in late fall or early spring, when the concentration of active compounds reaches its peak. During this time, the plant has redirected its energy reserves to the root system, resulting in higher levels of polyphenols, alkamides, and other bioactive compounds that contribute to the extract's therapeutic value.
Following harvest, immediate processing becomes paramount to preserve the integrity of heat-sensitive compounds. Fresh roots should be thoroughly cleaned to remove soil, debris, and any damaged portions that could compromise the extraction quality. The cleaning process involves gentle washing with cold water, followed by careful inspection to ensure only healthy, unblemished root material proceeds to the next stage.
The drying process requires particular attention to temperature and humidity control. Optimal drying occurs at temperatures between 40-50°C in well-ventilated conditions, allowing moisture content to reduce to approximately 8-12% while maintaining the structural integrity of bioactive compounds. This controlled drying environment prevents the degradation of sensitive polyphenols and preserves the characteristic yellow-brown color that indicates quality echinacea purpurea root extract material.
Size reduction through grinding or milling creates the optimal surface area for subsequent extraction procedures. The plant material should be processed to achieve a consistent mesh size, typically around 80 mesh, which provides the ideal balance between surface area exposure and material handling efficiency. This uniform particle size ensures consistent extraction rates and helps prevent the formation of channels that could lead to incomplete extraction of valuable compounds.
Extraction Methods
The selection of appropriate extraction methods determines the efficiency and quality of obtaining echinacea purpurea root extract. Various techniques have been developed and refined over time, each offering distinct advantages depending on the desired compound profile and intended application of the final extract.
Solvent extraction remains the most widely employed method for processing echinacea purpurea material. Water-based extraction, often conducted at elevated temperatures, effectively captures water-soluble compounds including polysaccharides and certain phenolic compounds. The process typically involves maintaining temperatures between 80-90°C for 2-3 hours while ensuring continuous agitation to maximize compound solubility. This method proves particularly effective for extracting the polyphenolic compounds that contribute to the characteristic 4% polyphenol specification commonly sought in commercial preparations.
Ethanol extraction offers superior versatility in capturing both hydrophilic and lipophilic compounds present in echinacea purpurea roots. Using ethanol concentrations ranging from 50-70%, this method can effectively extract alkamides, caffeic acid derivatives, and various polyphenolic compounds that contribute to the extract's bioactivity. The extraction process typically involves maceration periods of 24-48 hours at room temperature, followed by filtration and concentration procedures.

Supercritical fluid extraction using carbon dioxide represents an advanced technique that offers exceptional selectivity and produces solvent-free extracts. This method operates under specific pressure and temperature conditions, typically 200-300 bar and 40-60°C, allowing for precise control over compound extraction while maintaining the integrity of heat-sensitive bioactive molecules. The resulting extract demonstrates excellent purity and concentration of target compounds without residual solvent concerns.
Ultrasonic-assisted extraction has gained popularity for its ability to reduce processing time while improving extraction efficiency. Sound waves create cavitation bubbles that enhance mass transfer, allowing for more complete extraction of compounds from cellular structures. When applied to echinacea purpurea root material, this method can significantly reduce extraction time from hours to minutes while maintaining comparable or superior yield compared to traditional methods.
Microwave-assisted extraction represents another innovative approach that uses microwave energy to heat solvents and plant material simultaneously. This method creates rapid heating throughout the extraction matrix, leading to improved mass transfer and reduced processing time. The controlled heating environment helps preserve thermolabile compounds while achieving efficient extraction of polyphenolic compounds essential for high-quality echinacea purpurea root extract production.

Post-Extraction Processing
The transformation of crude extract into standardized echinacea purpurea root extract requires sophisticated post-extraction processing techniques. These procedures ensure product consistency, stability, and compliance with quality specifications while maintaining the bioactivity of essential compounds throughout the manufacturing process.
Filtration represents the initial step in post-extraction processing, removing particulate matter and insoluble components that could affect extract quality. Multi-stage filtration systems, beginning with coarse filtration to remove large particles and progressing to fine membrane filtration, ensure complete removal of unwanted materials while preserving valuable dissolved compounds. This process is particularly important for achieving the clear appearance and consistent quality expected in professional-grade extracts.

Concentration procedures concentrate the extract to desired potency levels while removing excess solvents. Vacuum evaporation at reduced temperatures prevents thermal degradation of sensitive compounds while efficiently removing water or ethanol used during extraction. The concentration process must be carefully monitored to achieve target specifications, such as the 4% polyphenol content that characterizes quality echinacea purpurea root extract preparations.
Spray drying converts liquid extracts into stable powder form, facilitating storage, handling, and incorporation into various formulations. The process involves atomizing the concentrated extract into fine droplets within a heated chamber, rapidly removing moisture while preserving compound integrity. Properly executed spray drying produces the characteristic yellow-brown powder appearance with 80 mesh particle size that indicates quality processing.

Quality control testing throughout post-extraction processing verifies extract purity, potency, and safety. Comprehensive analytical protocols include moisture content determination, microbial testing, heavy metal analysis, and pesticide residue screening. These quality assurance measures ensure the final echinacea purpurea root extract meets stringent safety and efficacy standards required for commercial applications.
Rebecca: China Echinacea Purpurea Root Extract Supplier
The extraction of echinacea purpurea requires careful attention to every stage of the process, from initial material preparation through final product standardization. Understanding these methodologies enables the production of high-quality extracts that maintain the therapeutic potential of this remarkable botanical resource.
Rebecca Bio-Tech stands as a trusted supplier of premium echinacea purpurea extract, offering standardized products that meet the highest quality standards. Our specialized extraction processes ensure optimal concentration of beneficial polyphenols while maintaining the natural integrity of this valuable botanical extract.
Ready to source premium echinacea purpurea root extract for your applications? Our technical team provides comprehensive support from product selection through application development. Contact our specialists today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how Rebecca Bio-Tech's quality commitment can enhance your product development success.
For detailed product information, technical specifications, or to place your order, please contact us at information@sxrebecca.com. Our experienced team looks forward to supporting your botanical extract needs with professional service and reliable quality.
References
Journal of Ethnopharmacology studies on echinacea preparation methods (2023); Phytochemistry International guidelines for botanical material processing (2024).
Food Chemistry research on echinacea extraction optimization (2023); Industrial Crops and Products comparative extraction studies (2024).
Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences post-extraction processing guidelines (2024); Quality Control in Herbal Medicine standardization protocols (2023).








