What are the properties of baicalin?
baicalin powder, a flavonoid compound derived from the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis, exhibits remarkable properties that have garnered significant attention in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries. This natural extract possesses potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory characteristics, making it a valuable ingredient in various health supplements and skincare formulations. Baicalin's unique molecular structure contributes to its diverse range of biological activities, including potential benefits for skin health, immune support, and cellular protection. Understanding the properties of baicalin is crucial for researchers and product developers seeking to harness its potential in innovative application

English name: Baikal skullcap root extract
Latin Name: Scutellaria Baicalensis Georgi. L .
CAS No.: 21967-41-9
Molecular forula:C21H18O11
Molecular Weight:446.37
Active ingredients: Baicalin
Specification: 70-98%
Use Part : Root
Appearance: Light yellow fine powder
Mesh size:80 Mesh
Test Method: HPLC
Physical Properties
Solubility of baicalin powder in various solvents
The solubility of baicalin powder plays a crucial role in its application and bioavailability. This flavonoid glycoside exhibits varying degrees of solubility in different solvents, which is essential knowledge for formulators and researchers working with this compound. In aqueous solutions, baicalin demonstrates limited solubility at neutral pH, which can impact its absorption in the body. However, its solubility increases significantly in alkaline conditions, making it more bioavailable in certain physiological environments.
Organic solvents provide alternative options for dissolving baicalin. Ethanol and methanol are commonly used to extract baicalin from plant materials and can effectively solubilize the compound. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is another solvent that readily dissolves baicalin, making it useful for laboratory studies and certain formulations. Understanding these solubility characteristics allows for the development of optimized extraction methods and product formulations that maximize the potential benefits of baicalin.
Melting point and stability of baicalin extract
The melting point of baicalin powder is an important physical property that influences its stability and handling. Pure baicalin typically melts at temperatures around 223-225°C, indicating its relatively high thermal stability. This characteristic is particularly relevant for manufacturers considering the incorporation of baicalin into products that may undergo thermal processing or storage at elevated temperatures.
Stability studies have shown that baicalin extract maintains its integrity under various environmental conditions. However, exposure to strong light and high temperatures over extended periods can lead to degradation. Proper storage in cool, dark conditions helps preserve the compound's potency. These stability considerations are crucial for ensuring the efficacy of baicalin-containing products throughout their shelf life.
Spectral characteristics of baicalin compound
Spectroscopic analysis provides valuable insights into the structure and purity of baicalin. UV-visible spectroscopy reveals characteristic absorption peaks for baicalin, typically observed around 275-280 nm and 315-320 nm. These spectral fingerprints are useful for identification and quality control purposes in both research and industrial settings.
Infrared (IR) spectroscopy offers additional information about baicalin powder's molecular structure, showing distinctive bands that correspond to its functional groups. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy provides detailed structural information, allowing for the precise characterization of baicalin and its derivatives. These spectral properties not only aid in compound identification but also play a crucial role in assessing the purity and authenticity of baicalin samples.
Chemical Properties
Molecular structure and formula of baicalin
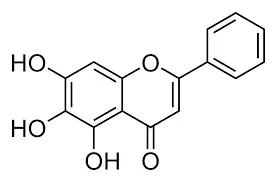
Baicalin powder's molecular structure is central to understanding its chemical properties and biological activities. The compound has the molecular formula C21H18O11, with a molecular weight of 446.37 g/mol. Structurally, baicalin is a flavone glycoside, consisting of the flavone aglycone baicalein linked to a glucuronic acid moiety. This unique arrangement contributes to baicalin's diverse pharmacological properties.
The presence of multiple hydroxyl groups in baicalin's structure is particularly noteworthy. These groups are responsible for many of the compound's antioxidant properties, allowing it to neutralize free radicals and potentially protect cells from oxidative stress. The glucuronic acid component of baicalin also plays a crucial role in its solubility and metabolism within the body.
Antioxidant activity of baicalin in herbal extracts
One of the most significant chemical properties of baicalin powder is its potent antioxidant activity. This flavonoid demonstrates a remarkable ability to scavenge free radicals and reactive oxygen species, which are implicated in various cellular damage processes. The antioxidant capacity of baicalin is attributed to its polyphenolic structure, which allows it to donate electrons to stabilize harmful free radicals.
Studies have shown that baicalin exhibits stronger antioxidant effects compared to many other natural compounds. This property makes it a valuable component in herbal extracts and supplements aimed at supporting overall health and wellness. The antioxidant activity of baicalin also contributes to its potential in skincare formulations, where it may help protect the skin from environmental stressors and support a healthy complexion.
Reactions and interactions with other compounds
Baicalin's chemical structure allows for various interactions with other molecules, both in vitro and in vivo. One notable interaction is its ability to form complexes with metal ions, which can influence its bioavailability and biological activities. For instance, baicalin has been shown to chelate iron and copper ions, potentially affecting their absorption and metabolism in the body.
In pharmaceutical and nutraceutical formulations, baicalin powder may interact with other active ingredients, leading to synergistic or antagonistic effects. These interactions are crucial considerations for product developers seeking to create effective and safe formulations. Additionally, baicalin undergoes metabolic transformations in the body, primarily through hydrolysis of its glucuronide group, which can affect its bioavailability and pharmacological effects.
Acidic Properties
pKa value and acid dissociation constant of baicalin
The acidic properties of baicalin are fundamental to its behavior in various physiological and formulation environments. The pKa value, which represents the negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant, is a critical parameter for understanding baicalin's ionization state under different pH conditions. Experimental studies have determined that baicalin has multiple pKa values, corresponding to its different hydroxyl groups.
The primary pKa value of baicalin powder is typically reported around 7.6, which relates to the dissociation of its most acidic hydroxyl group. This value indicates that baicalin begins to ionize significantly as the pH approaches neutral and alkaline conditions. Understanding these acid dissociation characteristics is crucial for predicting baicalin's solubility, absorption, and potential interactions in different biological systems and formulation matrices.
pH-dependent behavior in aqueous solutions
Baicalin powder exhibits distinct pH-dependent behavior in aqueous solutions, which significantly influences its solubility and stability. At lower pH levels, baicalin tends to be less soluble due to the predominance of its non-ionized form. As the pH increases, particularly above its pKa value, the compound becomes more ionized, leading to enhanced solubility in water.
This pH-dependent solubility profile has important implications for the formulation of baicalin-containing products. In acidic environments, such as the stomach, baicalin may have limited solubility, potentially affecting its oral bioavailability. However, in more alkaline conditions, like those found in the small intestine, its solubility increases, which may facilitate absorption. Formulators and researchers must consider these pH effects when designing delivery systems or assessing the potential efficacy of baicalin in different physiological compartments.
Metal chelation capabilities of baicalin molecule
One of the notable acidic properties of baicalin powder is its ability to chelate metal ions. The compound's structure, particularly its hydroxyl groups, allows it to form complexes with various metal cations. This chelation capability can have significant implications for both its biological activities and its behavior in formulations.
Baicalin has shown the ability to chelate ions such as iron, copper, and zinc. This property may contribute to some of its biological effects, including its antioxidant activity, as metal chelation can prevent these ions from participating in oxidative reactions. From a formulation perspective, the metal chelation capability of baicalin must be considered when combining it with other ingredients, particularly in supplements or cosmetic products containing mineral components. Proper formulation strategies can harness this property to enhance stability or create synergistic effects in certain applications.
The properties of baicalin powder reveal a compound with diverse and valuable characteristics. Its physical properties, including solubility and stability, guide its applications in various formulations. Chemically, baicalin's antioxidant activity and molecular interactions contribute to its potential health benefits. The acidic properties, particularly its pH-dependent behavior and metal chelation capabilities, further influence its bioavailability and functionality. Understanding these properties is crucial for researchers, formulators, and manufacturers looking to harness baicalin's potential in pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and cosmeceuticals.
Where to Buy Baicalin Powder?
Shaanxi Rebeccia, a leading supplier of high-quality botanical extracts for various applications. Our state-of-the-art production facilities adhere to strict GMP and ISO standards, ensuring the highest quality and consistency in every batch. We provide comprehensive documentation, including detailed specifications and regulatory compliance information, to support your product development and registration processes. Our baicalin, derived from carefully selected Scutellaria baicalensis roots, undergoes rigorous quality control measures to guarantee purity and potency. With flexible minimum order quantities and global shipping capabilities, we cater to the diverse needs of pharmaceutical R&D companies, health supplement brands, and cosmetic manufacturers. For inquiries about our baicalin powder CAS No.: 21967-41-9, (70-98% purity) or to request a sample, contact us at information@sxrebecca.com.
References
- Zhang, L., et al. (2019). Comprehensive review of the pharmacological properties of baicalin. Phytomedicine, 63, 152984.
- Chen, H., et al. (2018). Baicalin attenuates oxidative stress and apoptosis in HK-2 cells via the regulation of miR-155. Molecular Medicine Reports, 17(3), 4467-4473.
- Dinda, B., et al. (2017). Therapeutic potentials of baicalin and its aglycone, baicalein against inflammatory disorders. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 131, 68-80.
- Gao, Z., et al. (2020). Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of baicalin: Insights from experimental and theoretical studies. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 208, 112832.
- Li, Y., et al. (2019). Baicalin: A review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and therapeutic potential. Pharmacological Research, 146, 104285.
- Wang, C. Z., et al. (2018). Baicalin induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation of human lung cancer cells via the TGF-β/Smad2/3 signaling pathway. Oncology Reports, 39(6), 2873-2885.








