What is oat beta glucan?
Oat glucan is a soluble dietary fiber found naturally in oats. It's a key component that gives oats their renowned health benefits. oat beta glucan powder is a concentrated form of this fiber, extracted and purified from oat bran. This versatile ingredient has gained significant attention in the health and nutrition industry due to its potential to support heart health, blood sugar management, and immune function. With its unique molecular structure and impressive solubility, oat glucan powder offers a powerful nutritional boost to various food and beverage applications.

Product Name: Oat Extract, Oat Glucan, Oat Beta Glucan, Oat Glucan Powder
CAS No.9041-22-9
Specification: Oat Beta Glucan, 70%,80%,90%.
Appearance: White to light yellow powder
Latin Name: Avena Sativa L
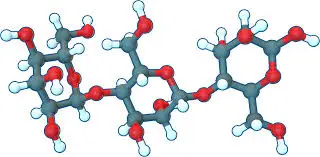
Molecular Structure Of Oat Beta GlucanChemical composition
Oat beta glucan is a complex polysaccharide composed of glucose molecules. These glucose units are linked together through β-(1→3) and β-(1→4) glycosidic bonds, forming a unique linear chain structure. This specific arrangement of glucose molecules is what sets oat beta-glucan apart from other dietary fibers and contributes to its exceptional properties.
Beta-glucan's unique linear and branched structure
While the primary structure of oat beta glucan is linear, it also contains occasional branches. These branches occur at the β-(1→3) linkages, creating a semi-flexible molecule. This combination of linear chains and occasional branching gives oat beta-glucan its distinctive characteristics, including its ability to form viscous solutions and interact with other molecules in the digestive system.
Molecular weight impacts oat beta glucan function
The molecular weight of oat beta glucan plays a crucial role in determining its functional properties. Higher molecular weight beta glucans tend to form more viscous solutions and may have a more significant impact on physiological responses. Research has shown that the molecular weight can influence factors such as cholesterol-lowering efficacy and blood glucose regulation. Manufacturers of oat glucan powder often carefully control the molecular weight to optimize its health benefits and functionality in various applications.
Oat beta glucan vs. other dietary fibers
Comparing solubility: Oat beta glucan's advantage
One of the standout features is its high solubility compared to many other dietary fibers. This solubility allows it to easily integrate into various food and beverage formulations without significantly altering texture or taste. When dissolved in water, oat beta glucan forms a viscous solution, which is believed to contribute to its physiological effects, such as slowing digestion and helping to regulate blood sugar levels.
Viscosity differences between fiber types
The viscosity of dietary fibers can vary significantly, and oat beta glucan is known for its ability to create highly viscous solutions. This property sets it apart from less viscous fibers like cellulose or inulin. The high viscosity of oat glucan solutions is thought to be a key factor in its cholesterol-lowering effects, as it may help to trap bile acids and prevent their reabsorption in the intestines.
Health benefits: Oat beta glucan vs. other fibers
While many dietary fibers offer health benefits, oat beta glucan has a particularly strong body of evidence supporting its positive effects on cardiovascular health and blood sugar management. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has approved health claims for oat glucan related to cholesterol reduction and post-meal glycemic responses. These authorized health claims distinguish oat extract from many other dietary fibers and highlight its potential as a functional ingredient in health-promoting food products.

How the body processes oat beta glucan?
Digestion and absorption of oat beta glucan
When consumed, oat beta glucan is not digested in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Instead, it passes through to the large intestine largely intact. This journey through the digestive system allows oat glucan to interact with various components of the gut, potentially influencing nutrient absorption and metabolic processes along the way. In the large intestine, oat extract undergoes fermentation by gut bacteria, producing short-chain fatty acids that may confer additional health benefits.
Beta glucan's interaction with gut microbiota
The fermentation of oat beta glucan by gut bacteria is a crucial aspect of its health-promoting effects. This process not only produces beneficial short-chain fatty acids but also may help to support a diverse and healthy gut microbiome. Research suggests that regular consumption of oat beta-glucan can lead to positive changes in the composition of gut bacteria, potentially contributing to improved digestive health and overall well-being.
Metabolic effects of oat beta glucan consumption
The consumption of oat beta glucan has been associated with several metabolic effects. These include a reduction in cholesterol levels, particularly LDL cholesterol, and improved blood sugar regulation. The mechanisms behind these effects are still being studied, but they likely involve a combination of factors, including the physical properties of oat glucan in the gut, its influence on nutrient absorption, and its interactions with gut bacteria. These metabolic effects underscore the potential of oat extract as a functional ingredient in foods aimed at supporting cardiovascular health and blood sugar management.
Oat beta glucan is a dietary fiber with unique properties that set it apart from other fibers. Its molecular structure, high solubility, and viscosity contribute to its numerous health benefits, particularly in supporting heart health and blood sugar regulation. As research continues to uncover the mechanisms behind its effects, oat beta-glucan powder is likely to play an increasingly important role in functional foods and dietary supplements. Its versatility and strong scientific backing make it a valuable ingredient for manufacturers looking to enhance the nutritional profile of their products.
China Oat Beta Glucan Powder Supplier
At Shaanxi Rebeccia, we pride ourselves on delivering premium oat glucan powder that meets the highest quality standards. Our state-of-the-art production facilities employ advanced extraction, separation, and purification technologies to ensure the purity and efficacy of our products. We adhere strictly to GMP and ISO standards throughout our manufacturing process, from raw material selection to final product delivery. Our oat beta glucan powder (CAS No.9041-22-9) is available in concentrations of 70%, 80%, and 90%, appearing as a white to light yellow powder. Derived from Avena Sativa L., our product offers the flexibility and quality that health supplement brands, functional beverage manufacturers, and pharmaceutical R&D companies demand. For inquiries about our oat glucan powder or to discuss how we can meet your specific needs, please contact us at information@sxrebecca.com. Experience the Shaanxi Rebeccia difference in quality, consistency, and customer service.
References
- Othman, R. A., Moghadasian, M. H., & Jones, P. J. (2011). Cholesterol-lowering effects of oat β-glucan. Nutrition Reviews, 69(6), 299-309.
- Lazaridou, A., & Biliaderis, C. G. (2007). Molecular aspects of cereal β-glucan functionality: Physical properties, technological applications and physiological effects. Journal of Cereal Science, 46(2), 101-118.
- Tosh, S. M., & Chu, Y. (2015). Systematic review of the effect of processing of whole-grain oat cereals on glycaemic response. British Journal of Nutrition, 114(8), 1256-1262.
- El Khoury, D., Cuda, C., Luhovyy, B. L., & Anderson, G. H. (2012). Beta glucan: health benefits in obesity and metabolic syndrome. Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, 2012, 851362.
- Wang, Q., & Ellis, P. R. (2014). Oat β-glucan: physico-chemical characteristics in relation to its blood-glucose and cholesterol-lowering properties. British Journal of Nutrition, 112(S2), S4-S13.
- Jayachandran, M., Chen, J., Chung, S. S. M., & Xu, B. (2018). A critical review on the impacts of β-glucans on gut microbiota and human health. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 61, 101-110.








