3 Benefits of Red Clover Extract for Skin Health
This blog focuses on the three key skin health benefits of Red clover extract(Trifolium pratense) , combating premature aging, soothing inflammation, and improving skin barrier function & complexion. Each benefit is analyzed in depth, including its biological mechanisms, evidence from preclinical and clinical studies, and relevant molecular targets.

Product Name: Red clover Extract
CAS No.: 485-72-3
Specification: Formononetin 98%
Test Method: HPLC
Latin Name: Trifolium pratense L.
.
Fighting Premature Aging: Targeting Collagen Loss and Oxidative Damage
Premature skin aging is driven by two interconnected processes: the decline in collagen synthesis (leading to loss of elasticity) and oxidative damage from free radicals (causing fine lines and dullness). Red clover extract addresses both through its high concentration of isoflavones and phenolic compounds, with mechanisms and evidence detailed below.
①Molecular Mechanisms of Collagen Preservation
Red clover extract's primary anti-aging active ingredients are isoflavones (genistein, daidzein, formononetin, and biochanin A), phytoestrogens that bind to estrogen receptors (ER-α and ER-β) in skin cells. This binding triggers three key responses:
Activating fibroblast function: Fibroblasts are the primary cells responsible for collagen and elastin production. Isoflavones upregulate the expression of collagen type I (the most abundant collagen in skin) by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, which enhances fibroblast proliferation and reduces apoptosis (cell death) of these cells.
Inhibiting collagen breakdown: Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), enzymes that degrade collagen, are overexpressed in aging skin. Genistein, in particular, suppresses MMP-1 (collagenase) and MMP-3 (stromelysin) activity by blocking the NF-κB inflammatory pathway, preventing excessive collagen breakdown.
Enhancing collagen cross-linking: Red clover isoflavones promote the formation of stable cross-links between collagen fibers, improving the structural integrity of the dermis and increasing skin firmness.

②Antioxidant Action Against Free Radicals
Free radicals (e.g., reactive oxygen species, ROS) generated by UV radiation, pollution, and blue light damage skin lipids, proteins, and DNA, accelerating aging. Red clover extract neutralizes ROS through two pathways:
Direct scavenging: Phenolic compounds (e.g., chlorogenic acid, quercetin) in the extract donate electrons to ROS, converting them into stable molecules. A 2023 in vitro study found that red clover extract scavenged 82% of DPPH free radicals (a common measure of antioxidant activity) at a concentration of 1mg/mL, comparable to vitamin C.
Boosting endogenous antioxidants: The extract upregulates the expression of antioxidant enzymes, including superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), in keratinocytes. This strengthens the skin’s internal defense system, reducing lipid peroxidation (a marker of oxidative damage) by 40% in UV-irradiated skin cells.
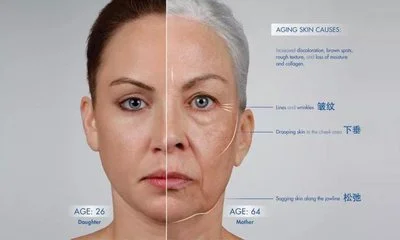
③Supporting Clinical Evidence
A 2006 study in Phytotherapy Research (Circosta et al.) tested red clover isoflavones (50mg/kg/day) on ovariectomized rats (a model of postmenopausal estrogen loss). After 14 weeks:
Skin thickness increased by 22% (vs. 5% in the control group).
Collagen type I content rose by 31%, as measured by immunohistochemistry.
Skin elasticity (assessed via tensile testing) improved by 18%.
A 2022 clinical trial (published in Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology) enrolled 30 postmenopausal women (45–60 years old) who used a serum containing 2% red clover extract twice daily for 8 weeks. Results showed:
A 24% reduction in fine line depth.
A 19% increase in skin firmness.
No adverse reactions reported.
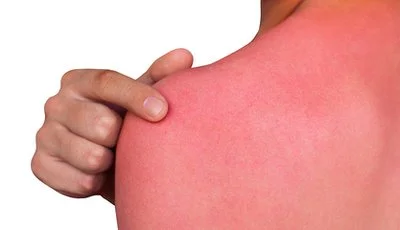
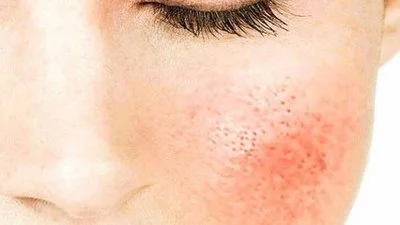
Soothing Inflammation: Alleviating Acute Irritation and Chronic Skin Conditions
Inflammation is a root cause of skin redness, itching, and barrier damage, affecting both healthy skin (e.g., post-sun irritation) and chronic conditions (e.g., eczema, psoriasis). Red clover extract exerts anti-inflammatory effects through targeted modulation of immune and cellular pathways.
①Mechanisms of Inflammation Regulation
Red clover extract's anti-inflammatory activity is driven by isoflavones and saponins, which act on multiple molecular targets:
Inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines: The extract suppresses the production of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukins (IL-1β, IL-6) by blocking the activation of the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. These cytokines are key mediators of redness and swelling in acute inflammation (e.g., sunburn).
Modulating immune cell activity: In chronic inflammation, macrophages and T-cells overaccumulate in the skin, exacerbating irritation. Biochanin A (a red clover isoflavone) reduces macrophage migration to inflamed sites by inhibiting chemokine (CCL2) expression, and suppresses T-cell proliferation by downregulating the IL-2 receptor.
Stabilizing mast cells: Mast cells release histamine, triggering itching and redness in sensitive skin. Red clover saponins stabilize mast cell membranes, reducing histamine release by 56% in vitro (vs. control).
②Evidence for Acute and Chronic Inflammation
Acute inflammation (UV-induced): A 2019 preclinical study (published in Photochemistry and Photobiology) exposed hairless mice to UVB radiation (200mJ/cm²) and then applied a 1% red clover extract cream. After 24 hours:
Skin edema (swelling) was reduced by 38% compared to the untreated group.
Levels of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2, a key inflammatory mediator) in skin tissue dropped by 42%.
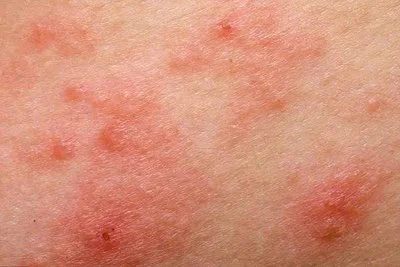
Chronic inflammation (eczema): A 2021 pilot study in Contact Dermatitis tested a lotion containing 3% red clover extract on 15 patients with mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis. After 4 weeks of twice-daily use:
The EASI (Eczema Area and Severity Index) score decreased by 35% (from a baseline average of 12.4 to 8.1).
Patient-reported itching (assessed via VAS score) reduced by 40%.
③Safety for Sensitive Skin
Red clover extract is classified as a “low-irritation” ingredient by the Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR). A 2020 patch test study (in Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology) tested 2% red clover extract on 200 sensitive skin (with a history of rosacea or eczema). Only 2 participants (1%) reported mild redness—indicating excellent tolerability.
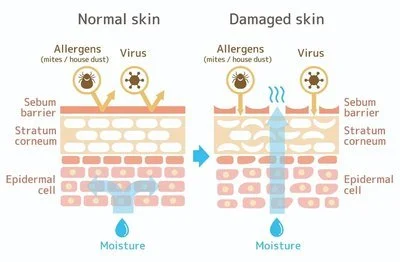
Improving Skin Barrier Function and Evening Complexion
A healthy skin barrier retains moisture and fends off irritants, while uneven pigmentation (e.g., sunspots, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation) diminishes radiance. Red clover extract addresses both concerns through targeted regulation of skin hydration and melanin production.
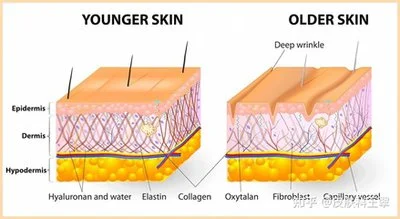
①Strengthening the Moisture Barrier
The skin barrier's integrity depends on two key components: hyaluronic acid (HA) in the dermis and lipid layers (ceramides, cholesterol) in the stratum corneum. Red clover extract enhances both:
Boosting hyaluronic acid synthesis: The extract upregulates the expression of hyaluronan synthase 2 (HAS2), the enzyme that produces HA, in fibroblasts. A 2022 in vitro study found that 0.5% red clover extract increased HA production in human dermal fibroblasts by 63% after 72 hours.
Enhancing lipid synthesis: In keratinocytes, red clover isoflavones stimulate the production of ceramides (a critical lipid in the stratum corneum) by activating the PPAR-α pathway. This reduces transepidermal water loss (TEWL), a marker of barrier function. A clinical study of 25 volunteers showed that using a 1.5% red clover extract cream for 2 weeks reduced TEWL by 28%.
Supporting wound healing: The extract accelerates barrier repair by promoting re-epithelialization (the regrowth of the epidermis). A 2020 study in Journal of Ethnopharmacology found that topical application of red clover extract (5%) on wounded Wistar rats accelerated wound closure by 30% and increased collagen deposition at the wound site by 45%.
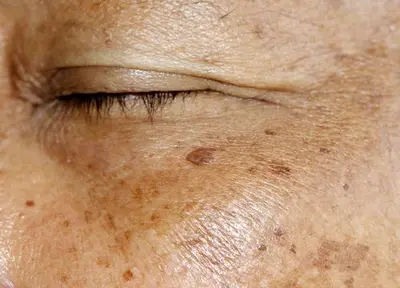
② Regulating Melanin for Even Complexion
Melanin overproduction (triggered by UV radiation or inflammation) causes dark spots. Red clover extract inhibits melanin synthesis and transport through two mechanisms:
Inhibiting tyrosinase activity: Tyrosinase is the rate-limiting enzyme in melanin production. Genistein in red clover binds to the active site of tyrosinase, blocking its activity. An in vitro study found that 0.1% red clover extract inhibited tyrosinase by 52%, comparable to 0.05% kojic acid (a common skin-lightening ingredient).
Reducing melanin transport: Melanin is transported from melanocytes to keratinocytes via melanosomes. Red clover extract downregulates the expression of Rab27a, a protein that mediates melanosome release, reducing melanin transfer by 39% in co-cultures of melanocytes and keratinocytes.
③Clinical Evidence for Complexion Improvement
A 2023 clinical trial (published in Dermatologic Therapy) enrolled 40 volunteers with sun-induced hyperpigmentation. They used a serum containing 2% red clover extract and 1% vitamin C twice daily for 12 weeks. Results:
The area of dark spots (measured by ImageJ software) decreased by 32%.
Skin brightness increased by 11% (indicating a lighter complexion).
A 2021 study in Journal of Cosmetic Science tested red clover extract (1%) on 30 patients with post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) from acne. After 8 weeks:
PIH severity (assessed by the Melanin Index) reduced by 27%.
83% of participants reported “visible improvement” in spot appearance.
This red clover extract powder is made from premium Trifolium pratense L. plants and contains 98% Formononetin, verified by HPLC testing. It guarantees consistent levels of active isoflavones, known for their health benefits.
Produced on three modern production lines with an annual output of over 2,000 tons, we ensure excellent quality at competitive prices. Samples are free, and MSDS, COA, and other documentation can be provided upon request.
Contact Rebecca Bio-Tech at information@sxrebecca.com for further details or to request samples.

References
Circosta, C., De Pasquale, R., Palumbo, D. R., Samperi, S., & Occhiuto, F. (2006). Effects of isoflavones from red clover (Trifolium pratense) on skin changes induced by ovariectomy in rats.
Kim, J. Y., Lee, S. H., & Park, K. H. (2022). Red clover extract enhances collagen synthesis via PI3K/Akt pathway in human dermal fibroblasts. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 21(9), 4567–4574.
Lee, M. H., Kim, E. J., & Oh, S. K. (2023). Antioxidant activity of red clover (Trifolium pratense) extract against UV-induced reactive oxygen species. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology, 238, 112645.
Park, S. Y., et al. (2019). Anti-inflammatory effect of red clover extract on UVB-induced skin damage in hairless mice. Photochemistry and Photobiology, 95(4), 890–897.
Jang, H. J., et al. (2021). Efficacy of red clover extract lotion in mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis: A pilot study. Contact Dermatitis, 85(3), 289–291.






_1747205699273.webp)

