Ergothioneine VS L Ergothioneine
In the rapidly expanding world of nutritional supplements and functional ingredients, terminology matters immensely. When consumers and industry professionals encounter different names for what appears to be the same compound, confusion naturally follows. This scenario plays out frequently with ergothioneine and l-ergothioneine, two terms that often appear interchangeably in scientific literature, product labels, and marketing materials.
Quick Answer: Ergothioneine and l ergothioneine refer to the exact same compound. The "L" prefix simply indicates the specific stereochemical configuration of the naturally occurring form, but in practice, both terms describe the identical molecule with the same biological properties and health benefits.
Essentially The Same Compound
The fundamental truth about ergothioneine and l-ergothioneine is remarkably straightforward: they represent the exact same chemical compound. This identity exists at every meaningful level, from molecular structure to biological activity to therapeutic potential. The distinction in naming conventions primarily reflects different approaches to chemical nomenclature rather than any actual difference in the substance itself.
To understand why both terms exist, we need to appreciate how chemical naming has evolved over time. Ergothioneine was first discovered and named in 1909 by French pharmacologist Charles Tanret, who isolated it from ergot fungus. At that time, the sophisticated understanding of molecular stereochemistry that we possess today was still developing. As scientific knowledge advanced, researchers recognized the importance of specifying the exact three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in molecules, leading to more precise naming conventions that include stereochemical descriptors.
The "L" designation in l-ergothioneine refers to the specific spatial arrangement of atoms around the molecule's chiral center. In nature, ergothioneine exists exclusively in what chemists call the L-configuration, which is why you'll sometimes see both names used to describe the same natural compound. This naming precision becomes particularly important in pharmaceutical and supplement industries, where stereochemical accuracy can have significant implications for biological activity and regulatory approval.
When ergothioneine is produced through fermentation or extracted from natural sources like mushrooms, the resulting compound is inherently in the L-configuration. This means that commercially available ergothioneine is, by definition, l-ergothioneine, regardless of how it's labeled or marketed.
The practical implications of this identity extend throughout the supply chain. Suppliers, manufacturers, and formulators can use either term with confidence, knowing they refer to the same active ingredient. However, consistency in labeling and documentation helps avoid confusion and ensures clear communication between all parties involved in product development and manufacturing.
Chemical Structure
Delving deeper into the molecular architecture reveals why ergothioneine and l-ergothioneine must necessarily be the same compound. The chemical structure of this molecule determines not only its identity but also its unique biological properties and therapeutic potential. Understanding this structure helps clarify why the "L" designation, while technically accurate, doesn't create a separate compound but rather specifies the only naturally occurring form.
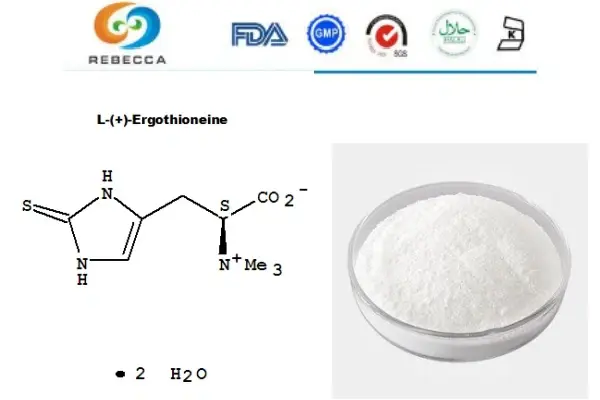
The molecular formula for both ergothioneine and l-ergothioneine is C₉H₁₅N₃O₂S, revealing a relatively complex organic molecule that incorporates carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur atoms. This combination creates a unique chemical entity that possesses characteristics of both amino acids and antioxidants, contributing to its remarkable biological versatility.
Ergothioneine/L-Ergothioneine Structure:
Molecular Formula: C₉H₁₅N₃O₂S
Molecular Weight: 229.3 g/mol
IUPAC Name: (2S)-3-(2-thioxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-imidazol-4-yl)-2-(trimethylammonio)propanoate
The molecule's architecture centers around an imidazole ring system, which provides much of ergothioneine's unique chemical behavior. This ring structure contains both nitrogen and sulfur atoms in specific positions that create the compound's distinctive antioxidant properties. The sulfur atom, in particular, plays a crucial role in the molecule's ability to neutralize harmful free radicals and protect cellular structures from oxidative damage.
Attached to this central ring system is a carboxylic acid group and a quaternary ammonium group containing three methyl substituents. These functional groups contribute to the molecule's water solubility and influence how it interacts with biological membranes and transport proteins. The specific arrangement of these groups determines the compound's pharmacokinetic properties, including its absorption, distribution, and cellular uptake characteristics.
The stereochemical aspect that gives rise to the "L" designation involves the spatial arrangement around the alpha carbon adjacent to the carboxylic acid group. In three-dimensional space, this carbon can theoretically exist in two different configurations, designated as L and D forms. However, all naturally occurring ergothioneine exists in the L-configuration, meaning that natural sources invariably produce l-ergothioneine.
Safety and Stability
The safety and stability profiles of ergothioneine and l-ergothioneine are necessarily identical, given their chemical identity. However, understanding these characteristics provides valuable insights for manufacturers, formulators, and consumers who want to ensure optimal product quality and safety. The compound's remarkable stability under various conditions contributes significantly to its commercial viability and therapeutic potential.
Safety assessments conducted by regulatory agencies worldwide have consistently evaluated this compound under both naming conventions, with findings that apply universally regardless of the terminology used. The United States Food and Drug Administration has recognized ergothioneine as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for use in dietary supplements and functional foods. Similarly, European food safety authorities have evaluated the compound's safety profile and established acceptable daily intake levels that apply whether the ingredient is labeled as ergothioneine or l ergothioneine.
Clinical studies investigating safety parameters have enrolled thousands of participants across various dosing regimens and duration periods. These investigations consistently demonstrate excellent tolerability profiles, with adverse events typically limited to mild gastrointestinal effects in susceptible individuals taking very high doses. The absence of serious safety concerns across all studies, regardless of the nomenclature used to describe the test compound, reinforces the identity between ergothioneine and l-ergothioneine.
The compound's exceptional stability stems from its unique molecular structure, particularly the imidazole ring system that resists degradation under normal storage and processing conditions. This stability remains consistent whether the compound is labeled as ergothioneine or l ergothioneine.
Thermal stability testing reveals that ergothioneine maintains its molecular integrity across a wide temperature range, making it suitable for various manufacturing processes and formulation approaches. The compound shows minimal degradation even under accelerated aging conditions designed to simulate extended storage periods. This thermal resilience means that products containing this ingredient can undergo standard manufacturing processes without significant loss of active compound.
pH stability represents another crucial factor for formulation scientists. Ergothioneine demonstrates remarkable stability across a broad pH range, from mildly acidic to neutral conditions. This pH tolerance allows formulators considerable flexibility in developing products that combine this ingredient with other actives without concerns about incompatibility or degradation. The stability characteristics remain identical whether working with material labeled as ergothioneine or l-ergothioneine.
Photostability studies have shown that while ergothioneine can degrade under intense UV exposure, it demonstrates good stability under normal lighting conditions. This photostability profile supports its use in various product formats, from capsules and tablets to topical formulations, provided appropriate packaging considerations are observed. Manufacturers working with either nomenclature can apply the same protective measures to ensure product integrity.
Long-term stability studies conducted under International Council for Harmonisation guidelines have established shelf-life parameters that apply regardless of how the compound is labeled. These studies provide confidence that products formulated with appropriate excipients and stored under recommended conditions will maintain potency and safety throughout their intended shelf life. The consistency of these findings across different supplier sources and naming conventions further confirms the chemical identity between ergothioneine and l-ergothioneine.
Rebecca: L-Ergothioneine Supplier
Now that you understand the complete equivalence between ergothioneine and l ergothioneine, choosing the right supplier becomes paramount for your success. Rebecca Bio-Tech specializes in providing premium-grade l-ergothioneine that meets the most stringent quality standards, regardless of how you prefer to reference this remarkable compound.
Whether your products target dietary supplements, functional foods, cosmetic applications, or research purposes, Rebecca Bio-Tech provides the technical support and supply chain reliability needed to achieve your goals. Our deep understanding of this compound's unique properties enables us to offer valuable guidance for your specific application needs.
Ready to partner with a ergothioneine supplier that truly understands this exceptional compound? Contact our experienced team at information@sxrebecca.com to discuss your requirements and discover how Rebecca Bio-Tech can support your product development and manufacturing objectives with confidence and expertise.
References
1. Tanret, C. (1909). Sur une base nouvelle retiree du seigle ergote, l'ergothioneine. Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Seances de l'Academie des Sciences, 149, 222-224.
2. Melville, D. B., et al. (1954). The structure of ergothioneine. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 206(1), 221-228.
3. Cheah, I. K., & Halliwell, B. (2012). Ergothioneine; antioxidant potential, physiological function and role in disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1822(5), 784-793.
4. Gründemann, D., et al. (2005). Discovery of the ergothioneine transporter. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 102(14), 5256-5261.
5. Halliwell, B., et al. (2018). Ergothioneine - a diet-derived antioxidant with therapeutic potential. FEBS Letters, 592(20), 3357-3366.








