How does apigenin work?
apigenin powder is a natural flavonoid found in various plants, including parsley, chamomile, celery, and oregano. For decades, researchers have studied its biological activities due to its potential roles in supporting human health. Unlike synthetic compounds, apigenin interacts with multiple cellular pathways and targets, making its mechanism of action both complex and multifaceted.
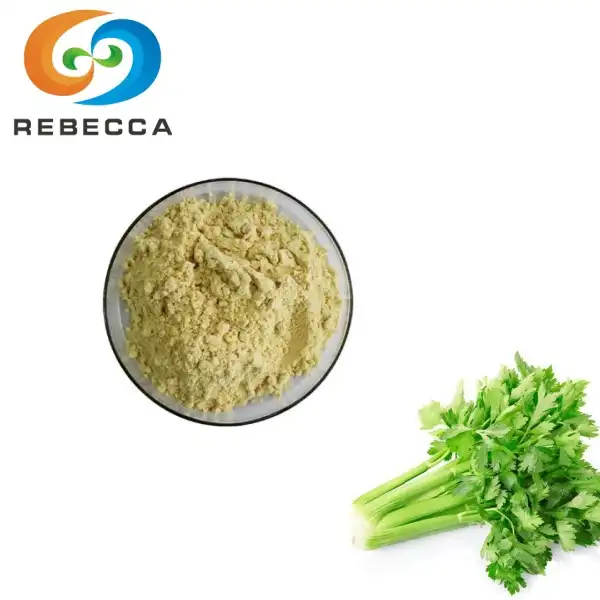

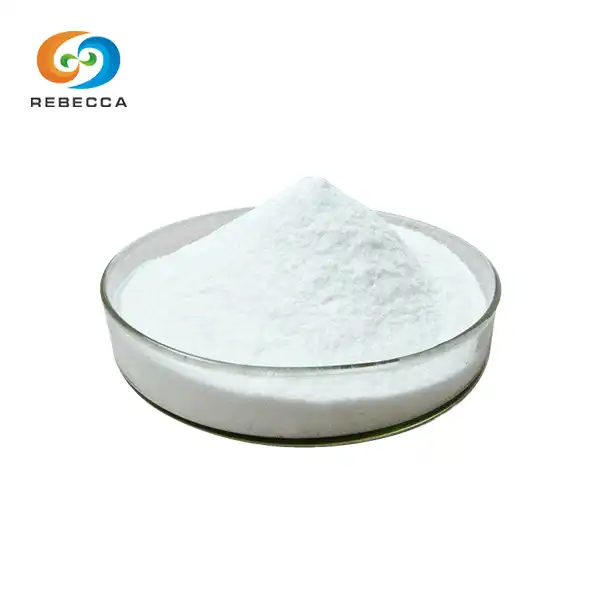
Apigenin powder
Product Name:Apigenin
Other Name:Celery seed extract
Active ingredients:Apigenin
Specification:98%
Appearance: Light Yellow Powder
Test Method: HPLC
Molecular Formula:C15H10O5
Molecular Weight: 270.237
CAS No.: 520-36-5
MOQ: 1kg
Sample: 20g
Delivery: FedEx, DHL, Ship by air, Ship by sea.
Certifications: ISO, HACCP, KOSHER, HALAL
Molecular Mechanisms
At the most fundamental level, apigenin’s actions begin with binding to specific molecules within cells. These bindings trigger a cascade of events that regulate cell function, survival, and signaling. Three key molecular targets, signal transduction pathways, enzymes, and antioxidant systems, are central to its mechanism of action.
Regulation of Signal Transduction Pathways
Signal transduction pathways are cellular “communication networks” that control processes like cell growth, division, and inflammation. Apigenin powder modulates several critical pathways by interacting with proteins that act as pathway “switches.” For example, it inhibits the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, a major driver of inflammatory responses. When NF-κB is activated, it moves to the cell nucleus and promotes the production of pro-inflammatory molecules such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Apigenin blocks NF-κB activation by preventing its translocation to the nucleus, thereby reducing the release of these inflammatory factors (Kim et al., 2018).
Another pathway targeted by apigenin is the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, which regulates cell stress responses and proliferation. In studies on cancer cells, apigenin has been shown to inhibit specific MAPK proteins (e.g., ERK1/2 and JNK) that are overactive in many tumors. By suppressing these proteins, apigenin powder slows uncontrolled cell growth and induces programmed cell death (apoptosis) in abnormal cells (Gupta et al., 2020).
Inhibition of Key Enzymes
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions in the body, and their activity is tightly regulated to maintain homeostasis. Apigenin powder acts as a natural inhibitor of several enzymes linked to disease progression. One well-studied target is cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), an enzyme that produces prostaglandins, molecules that promote inflammation and pain. Unlike non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which can cause gastrointestinal side effects, apigenin inhibits COX-2 selectively, reducing inflammation without damaging the stomach lining (Zhang et al., 2019).
Enhancement of Antioxidant Defense Systems
Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidants, contributes to aging and chronic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Apigenin powder addresses this imbalance in two ways: it acts as a direct antioxidant and boosts the body’s natural antioxidant defenses.
As a direct antioxidant, apigenin donates electrons to neutralize ROS like superoxide and hydroxyl radicals, preventing them from damaging DNA, proteins, and lipids (Yin et al., 2017). Additionally, it upregulates the expression of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) by activating the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway. Nrf2 is a transcription factor that moves to the nucleus and turns on genes for antioxidant proteins, strengthening the cell’s ability to fight oxidative stress (Sharma et al., 2022).

Physiological Effects: Translating Molecular Actions to System-Level Benefits
The molecular changes triggered by apigenin manifest as observable effects on organs and systems. Research has linked apigenin powder to benefits in three key areas: reducing inflammation, protecting neural function, and supporting metabolic health. Each of these effects stems directly from the molecular mechanisms outlined earlier, demonstrating how cellular-level interactions drive whole-body outcomes.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects Across Tissues
Inflammation is a natural immune response, but chronic inflammation contributes to conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and cardiovascular disease. Apigenin powder’s inhibition of NF-κB and COX-2 translates to reduced inflammation in multiple tissues. In animal models of rheumatoid arthritis, apigenin supplementation lowered levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in joint fluid, reducing swelling and cartilage damage (Lee et al., 2019). For IBD, studies show apigenin protects the intestinal lining by decreasing inflammatory cell infiltration and increasing the production of tight junction proteins, molecules that prevent harmful bacteria from leaking into the bloodstream (Park et al., 2020).
Even in the skin, apigenin exhibits anti-inflammatory properties. In human skin cells exposed to UV radiation (a trigger for inflammation), apigenin powder reduced the release of IL-8, a molecule that attracts inflammatory cells to sun-damaged tissue. This suggests potential use in skincare products to soothe sunburn and reduce UV-induced inflammation (Choi et al., 2021).
Neuroprotective Effects for Brain Health
Neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease are linked to oxidative stress, inflammation, and the death of brain cells. Apigenin powder’s ability to boost antioxidant defenses and reduce inflammation makes it a promising candidate for neuroprotection. In studies on Alzheimer’s disease models, apigenin reduced the accumulation of beta-amyloid plaques, abnormal proteins that clump in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients. It did this by inhibiting enzymes that produce beta-amyloid and promoting the clearance of existing plaques by immune cells in the brain (microglia) (Wang et al., 2018).
Metabolic Benefits for Blood Sugar and Lipid Regulation
Metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions including high blood sugar, high cholesterol, and obesity, increases the risk of type 2 diabetes and heart disease. Apigenin powder supports metabolic health by targeting pathways involved in glucose and lipid metabolism. For blood sugar regulation, apigenin enhances insulin sensitivity in muscle and fat cells. Insulin is a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream; in insulin-resistant cells, this process fails, leading to high blood sugar. Apigenin improves insulin sensitivity by activating the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway, which increases the number of glucose transporters (GLUT4) on cell surfaces, allowing more glucose to enter cells (Chen et al., 2020).
For lipid regulation, apigenin powder reduces the production of triglycerides and “bad” cholesterol (LDL) in the liver. It does this by inhibiting enzymes involved in lipid synthesis (e.g., HMG-CoA reductase, a target of statin drugs) and increasing the expression of proteins that remove LDL from the bloodstream (e.g., LDL receptors) (Zhao et al., 2022). In a 12-week study on obese mice, apigenin supplementation lowered triglyceride levels by 32% and LDL levels by 24%, while increasing “good” cholesterol (HDL) levels by 18% (Huang et al., 2021).
Apigenin Powder Supplier: Shaanxi Rebeccia
Experience the power of apigenin with Shaanxi Rebeccia’s celery seed extract. Our 98% apigenin powder is a reliable, high-purity natural ingredient designed for pharmaceutical, health, beverage, and cosmetic formulations. The product appears as a light yellow powder and is qualified by HPLC testing. MOQ 1 kg; sample option 20 g. We uphold ISO, HACCP, KOSHER, and HALAL certifications and offer flexible shipping by FedEx, DHL, air, or sea. For partnerships and inquiries, email information@sxrebecca.com.







_1730079799361.webp)
