What is gastrodia elata extract used for?
Gastrodia elata extract, derived from the orchid-like plant native to East Asia, has gained significant attention in the health and wellness industry. This potent extract is renowned for its diverse applications, particularly in supporting neurological health. Rich in bioactive compounds, it is primarily used to promote cognitive function, alleviate stress, and enhance overall brain health. Its potential benefits extend to improving sleep quality, reducing inflammation, and supporting cardiovascular health, making it a versatile ingredient in various health supplements and functional foods.

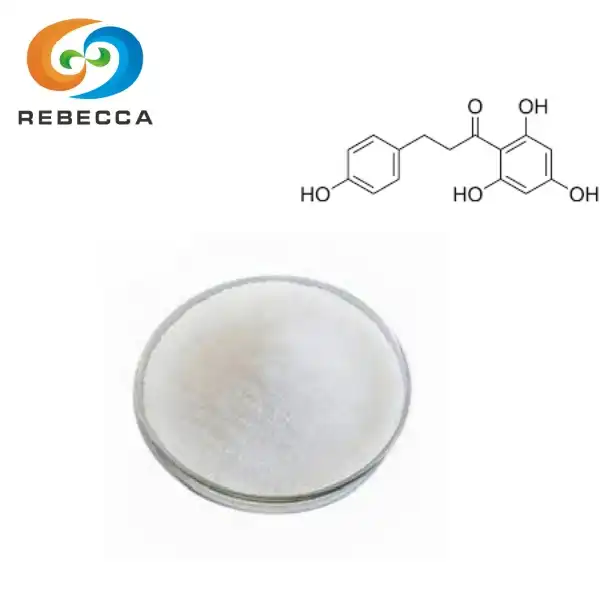
Gastrodia Elata Extract
【English name】:Gastrodin
【Latin Name】:Gastrodiae Rhizoma
【CAS No.】:62499-27-8
【Molecular Formula】: C13H18O7
【Active ingredients】: Gastrodin
【Specification】: 1%-99% Gastrodin
【Use Part】 :Rhizome
【Appearance】: Brown yellow to white powder
【Test Method】: HPLC
Traditional applications in Eastern medicine
Ancient Chinese remedies for neurological disorders
In traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), gastrodia elata, known as "Tian Ma," has been a cornerstone remedy for neurological disorders for centuries. This revered herb was often prescribed to address a range of conditions affecting the nervous system. Ancient practitioners recognized its ability to calm the liver and extinguish wind, concepts that in TCM correlate with neurological balance and stability.
The use of gastrodia elata extract in treating tremors, numbness, and vertigo was well-documented in classical TCM texts. These applications align with modern understanding of its neuroprotective properties. Historical records show that it was often combined with other herbs to create potent formulations for complex neurological issues, demonstrating an early understanding of synergistic herbal interactions.
Gastrodia elata's role in treating headaches and dizziness
One of the most prominent traditional uses of gastrodia elata extract was in alleviating headaches and dizziness. TCM practitioners observed its effectiveness in reducing the frequency and intensity of migraines, a finding that has sparked interest in contemporary research. The extract's ability to improve blood circulation to the brain was thought to be a key factor in its efficacy against these common complaints.
Historical texts describe various preparation methods for gastrodia elata, including decoctions and powders, tailored to treat different types of headaches. Its use was not limited to acute relief; it was also prescribed as a preventive measure for those prone to chronic headaches and vertigo, highlighting its perceived long-term benefits in Eastern medicine.
Historical use for epilepsy and convulsions management
Another significant traditional application of gastrodia elata extract was in managing epilepsy and convulsions. Ancient Chinese medical texts described its use in calming seizures and reducing their frequency. This application was rooted in the TCM concept of "calming the liver and subduing yang," which in modern terms can be interpreted as modulating neurotransmitter activity and reducing excessive neuronal firing.
The historical use of gastrodia elata for these conditions often involved complex formulations, combining it with other herbs known for their calming properties. This holistic approach to treating neurological disorders underscores the sophisticated understanding of herbal interactions in traditional Eastern medicine, setting the stage for modern research into its mechanisms of action.

Modern research on neurological benefits
Gastrodin: The key bioactive compound in gastrodia elata
Modern scientific investigations have identified gastrodin as the primary bioactive compound in gastrodia elata extract. This phenolic glycoside has become the focus of numerous studies exploring the extract's neurological benefits. Research has shown that gastrodin can cross the blood-brain barrier, directly influencing brain function and neurochemistry.
Studies have revealed gastrodin's multiple mechanisms of action, including modulation of neurotransmitter systems, particularly GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid). This action is thought to contribute to its calming and anti-anxiety effects. Additionally, gastrodin has demonstrated antioxidant properties, protecting neurons from oxidative stress and potentially slowing age-related cognitive decline.
Potential neuroprotective effects in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's
Recent research has explored the potential of gastrodia elata extract in addressing neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Preliminary studies suggest that the extract may help reduce the accumulation of beta-amyloid plaques, a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease. In Parkinson's disease models, gastrodin has shown promise in protecting dopaminergic neurons, which are critical for motor function.
While these findings are encouraging, it's important to note that most studies have been conducted in vitro or on animal models. Human clinical trials are still in their early stages, and more research is needed to fully understand the extract's efficacy and safety profile in treating these complex neurological conditions.
Anti-inflammatory properties and cognitive enhancement studies
The anti-inflammatory properties of gastrodia elata extract have been a subject of growing interest in the scientific community. Chronic inflammation is increasingly recognized as a contributing factor to cognitive decline and various neurological disorders. Studies have shown that compounds in the extract can suppress inflammatory markers and potentially protect brain tissue from inflammation-induced damage.
Cognitive enhancement is another area where gastrodia elata extract shows promise. Research has indicated potential improvements in memory, learning, and overall cognitive function. These effects are thought to be mediated through multiple pathways, including enhanced cerebral blood flow, modulation of neurotransmitter systems, and neuroprotection against oxidative stress.

How to incorporate gastrodia elata in daily life
Gastrodia elata supplements: Dosage and safety considerations
Incorporating gastrodia elata extract into daily routines typically involves dietary supplements. These are available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and powders. When considering supplementation, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine appropriate dosage and assess potential interactions with existing medications or health conditions.
While generally regarded as safe, gastrodia elata supplements should be used with caution. Current research suggests that dosages between 500-1000 mg per day are common in clinical studies, but individual needs may vary. It's important to start with lower doses and gradually increase if needed. Pregnant or nursing women, and individuals with specific health conditions, should exercise extra caution and seek medical advice before use.
Integrating gastrodia extract into functional beverages
The versatility of gastrodia elata extract allows for its integration into functional beverages, offering a convenient and enjoyable way to incorporate its benefits into daily routines. Some innovative beverage manufacturers are exploring the addition of this extract to create drinks that support cognitive function and stress relief.
When developing functional beverages with gastrodia extract, factors such as taste, stability, and bioavailability must be considered. The extract's mild flavor profile makes it suitable for blending with various beverage bases. However, proper formulation is key to ensure the active compounds remain stable and effective throughout the product's shelf life.

Exploring gastrodia-based skincare for anti-aging benefits
The potential benefits of gastrodia elata extract extend beyond internal use, with growing interest in its application in skincare products. Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties make it a promising ingredient for anti-aging formulations. Some cosmetic companies are incorporating the extract into serums, creams, and masks aimed at reducing signs of skin aging.
Research into the topical application of gastrodia extract is still in its early stages. Preliminary studies suggest it may help protect skin cells from oxidative stress and support collagen production. However, more comprehensive clinical trials are needed to fully understand its efficacy and optimal concentration in skincare products.
Gastrodia elata extract emerges as a versatile and promising natural ingredient with a wide range of potential applications. From its traditional roots in Eastern medicine to modern scientific investigations, this extract continues to intrigue researchers and health enthusiasts alike. Its neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, and cognitive-enhancing properties make it a valuable subject for ongoing research in neurological health. As interest grows, we can expect to see more innovative applications in supplements, functional foods, and even skincare products. However, it's crucial to approach its use with informed caution, always prioritizing safety and seeking professional guidance when considering supplementation.

Gastrodia Elata Extract Manufacturer
With three advanced production lines and an annual capacity of over 2,000 tons, we provide high-quality gastrodin powder at competitive prices. Our Gastrodin, derived from Gastrodiae Rhizoma rhizomes, is available in 1%-99% purity and tested by HPLC. Free samples and complete documentation (MSDS, COA) are available upon request. For more details or to request samples, contact Rebecca Bio-Tech at information@sxrebecca.com.
References
- Chen, P. J., et al. (2018). "Gastrodia elata Blume and its components as therapeutic agents for neurodegenerative diseases." Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 215, 217-226.
- Liu, Y., et al. (2019). "Neuroprotective effects of gastrodin: A review of molecular mechanisms." Frontiers in Pharmacology, 10, 1222.
- Zhang, X., et al. (2020). "Gastrodia elata Blume: A review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology." Phytomedicine, 76, 153261.
- Wang, H., et al. (2017). "Gastrodin ameliorates Parkinson's disease by downregulating connexin 43." Molecular Medicine Reports, 15(6), 4423-4428.
- Jang, J. H., et al. (2015). "Neuroprotective effects of Gastrodia elata Blume on neuronal cell damage in hippocampus following transient global ischemia in gerbils." Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 172, 121-129.
- Luo, L., et al. (2016). "Gastrodin: A novel therapeutic agent for oxidative stress-induced diseases." Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2016, 8950384.








