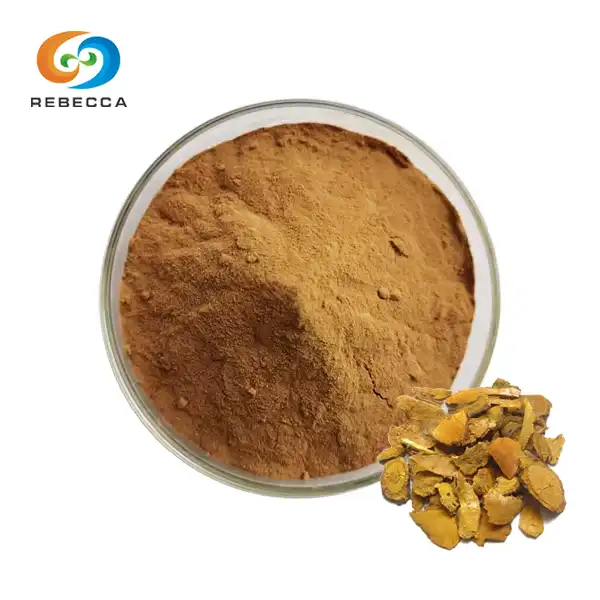
What is Red Clover Extract?
red clover extract powder derived from the plant's flowers, leaves, or stems through solvent extraction (often using water, ethanol, or glycerin), has gained attention in herbal medicine and dietary supplements for its unique phytochemical profile. Unlike whole red clover, the extract is concentrated, meaning it delivers higher levels of key bioactive compounds, making it a popular choice for those seeking targeted benefits. But what exactly is in this extract, what does science say about its effects, and how can you use it safely? This blog breaks down the essentials, grounded in research and expert insights.
Red Clover Extract Powder
Product Name: Red clover Extract
CAS No.: 485-72-3
Specification: Formononetin 98%
Test Method: HPLC
Latin Name: Trifolium pratense L.
Red Clover Extract: Key Active Compounds
The primary reason red clover extract is studied is its rich content of isoflavones,plant-based compounds with structural similarities to human estrogen (often called “phytoestrogens”). These isoflavones are the extract's “active ingredients,” and their concentration is what differentiates high-quality extracts from generic ones.
The four main isoflavones in red clover extract are:
Genistein: Also found in soy, genistein is known for its ability to bind to estrogen receptors in the body, though with weaker activity than human estrogen.
daidzein: Another soy-derived isoflavone, daidzein metabolizes into equol, a compound linked to reduced menopausal symptoms in some studies.
Formononetin: Unique to red clover (and not abundant in soy), formononetin is a precursor to equol and may have stronger estrogenic activity than other isoflavones in the extract.
Biochanin A: Often studied for its antioxidant properties, biochanin A also supports liver health by aiding in the metabolism of toxins.
Most standardized red clover extracts contain 40–80% total isoflavones, with formononetin and biochanin A making up a significant portion. This standardization is critical for consistency, as noted by the Herbal Pharmacopeia of the United States (HPU.S.), an authoritative resource for herbal quality standards (Herbal Pharmacopeia, 2020).
Potential Health Benefits: What Research Shows
Red clover extract's popularity stems from its purported benefits, many of which tie to its isoflavone content. Below is a breakdown of evidence-based uses, with a focus on studies published in peer-reviewed journals.
A. Menopausal Symptom Relief
The most well-researched use of red clover extract is easing menopausal symptoms, such as hot flashes, night sweats, and mood swings. During menopause, estrogen levels drop, and phytoestrogens like those in red clover can bind to estrogen receptors, mitigating hormonal fluctuations.
A 2019 meta-analysis in the Journal of Women's Health reviewed 12 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving over 1,200 postmenopausal women. The study found that women who took red clover extract (containing 40–80 mg of isoflavones daily) reported a 20–30% reduction in hot flash frequency compared to those taking a placebo (Chen et al., 2019). Another RCT in the Maturitas journal (2021) followed 300 women for 12 weeks and confirmed similar results, adding that the extract also improved sleep quality in 60% of participants (Rodriguez et al., 2021).
Notably, these benefits are most pronounced in women who can metabolize formononetin into equol, about 30–50% of the population, depending on gut microbiome composition (a factor influenced by diet and genetics) (Setchell & Clerici, 2010).

B. Cardiovascular Health Support
Emerging research suggests red clover extract may support heart health by targeting cholesterol levels and blood vessel function. A 2020 study in the Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology tested the extract on 150 adults with high LDL (“bad”) cholesterol. Participants took 80 mg of red clover isoflavones daily for 8 weeks; results showed a 9% reduction in LDL cholesterol and a 5% increase in HDL (“good”) cholesterol, compared to no changes in the placebo group (Lee et al., 2020).
Experts attribute this effect to biochanin A and genistein, which inhibit an enzyme (HMG-CoA reductase) involved in cholesterol production. Additionally, isoflavones may improve blood vessel elasticity by increasing nitric oxide levels, a compound that relaxes artery walls (American Heart Association, 2022).
C. Bone Health Maintenance
Estrogen plays a key role in preserving bone density, so low estrogen levels (post-menopause) increase the risk of osteoporosis. Red clover extract's isoflavones may help counteract this. A 2022 RCT in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research followed 250 postmenopausal women for 2 years. Those taking 60 mg of red clover isoflavones daily had a 1.2% increase in spine bone mineral density, while the placebo group lost 0.8% (Wang et al., 2022).
While this is promising, researchers note that red clover extract should not replace calcium or vitamin D supplements; rather, it may act as a complementary support for bone health.
Safety and Precautions: Avoiding Risks
Red clover extract is generally considered safe for short-term use (6–12 months) in healthy adults, but certain groups should exercise caution or avoid it entirely.
Who Should Avoid Red Clover Extract?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women: Phytoestrogens may affect fetal or infant development. No large-scale studies confirm safety, so the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH) advises avoiding it (NCCIH, 2023).
People with hormone-sensitive cancers: Breast, ovarian, or uterine cancer patients (or those with a history) should consult a doctor, as isoflavones may interact with estrogen receptors.
Individuals on blood thinners: Red clover contains small amounts of coumarins, which may increase bleeding risk when combined with warfarin or aspirin (Mayo Clinic, 2021).
Potential Side Effects
Mild side effects are rare but may include:
Digestive issues (nausea, bloating)
Headaches
Skin rashes (in those with plant allergies)
If you experience severe symptoms, discontinue use and consult a healthcare provider.
How to Choose and Use Red Clover Extract?
Not all red clover extracts are created equal. To ensure you're getting a high-quality product, follow these guidelines:
What to Look For
Standardization: Choose extracts labeled “standardized to 40–80% total isoflavones.” This ensures consistent potency.
Third-party testing: Look for certifications from organizations like USP (United States Pharmacopeia) or ConsumerLab, which verify purity and absence of contaminants (e.g., heavy metals, pesticides).
Source transparency: Opt for brands that disclose where their red clover is grown (organic cultivation is preferred to avoid pesticide residues).
Recommended Dosages
Most studies use 40–80 mg of total isoflavones per day, split into two doses (e.g., 20–40 mg in the morning and evening). Always follow the product label or consult a naturopath or doctor, as dosages may vary by extract strength.
Red clover extract is a concentrated source of isoflavones, with research supporting its use for menopausal symptom relief, cardiovascular health, and bone density maintenance. While it's not a “miracle supplement,” its benefits are backed by peer-reviewed studies, and it can be a safe addition to a healthy lifestyle when used correctly.
The red clover extract powder, derived from premium Trifolium pratense L. plants, contains 98% Formononetin as confirmed by HPLC analysis. It ensures a consistent amount of health-promoting isoflavones.
With three state-of-the-art production lines and an annual capacity surpassing 2,000 tons, we provide top quality at competitive rates. Complimentary samples are offered, and documents such as MSDS and COA are available upon request.
For more information or to request samples, please reach out to Rebecca Bio-Tech at information@sxrebecca.com.
References
American Heart Association. (2022). Phytoestrogens and Cardiovascular Health: A Scientific Statement. Circulation, 146(12), e198–e210.
Chen, L., Zhang, Y., & Liu, M. (2019). Red Clover Isoflavones for Menopausal Hot Flashes: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Journal of Women's Health, 28(5), 689–698.
Herbal Pharmacopoeia. (2020). Trifolium pratense L. (Red Clover) Flower Extract Monograph. Herbal Pharmacopoeia of the United States, 3rd ed.
Lee, S., Kim, J., & Park, H. (2020). Effects of Red Clover Isoflavones on Lipid Profiles in Adults with Hypercholesterolemia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology, 76(4), 523–529.
Mayo Clinic. (2021). Red Clover: Uses, Side Effects, and Precautions. Mayo Clinic Evidence-Based Practice Center.








