What is the difference between berberine and berberine hcl?
Berberine and berberine HCl are closely related compounds, but they have distinct characteristics that set them apart. The main difference lies in their chemical structure and properties. Berberine is an alkaloid compound found naturally in various plants, while HCl (hydrochloride) is the salt form of berberine. This salt formation significantly enhances the compound's solubility and bioavailability, making it more readily absorbed by the body. As a result, HCl is often preferred in dietary supplements and research studies for its improved efficacy and stability.
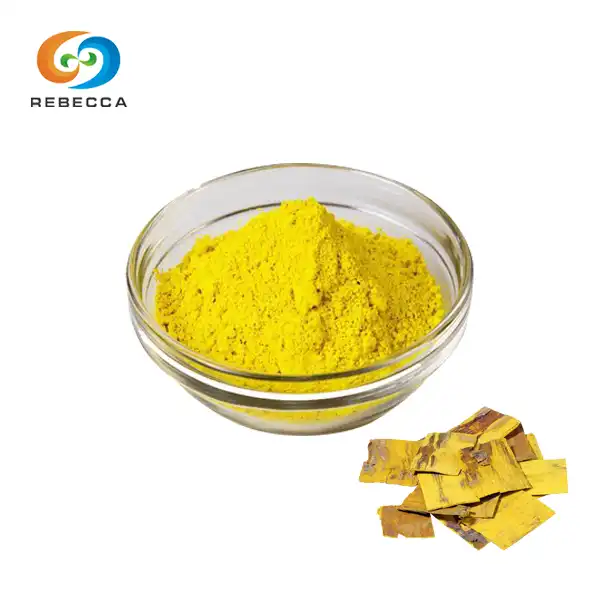

【English name】: Berberine HCL
【Latin Name】: Cortex Phellodendri Chinensis.
【CAS No.】: 633-65-8
【Molecular Formula】: C20H18ClNO4
【Active ingredients】: Berberine,phellodendrine,magnoflorine, jatrorrhizine,palmatine etc.
【Specification】: 97%
【Use Part】 : Bark
【Appearance】: Yellow crystalline powder
【Mesh size】:80 Mesh
【Test Method】: HPLC,Titration Test
Chemical Structure: Berberine vs Berberine HClMolecular composition of berberine and its HCl salt
Berberine, in its pure form, is an isoquinoline alkaloid with the molecular formula C20H18NO4+. It features a distinctive yellow color and a bitter taste. The molecular structure of berberine consists of a quaternary ammonium salt with a planar, aromatic ring system.
Berberine HCl, on the other hand, has the molecular formula C20H18ClNO4. The addition of hydrochloride (HCl) to berberine creates a salt form, which alters its physical and chemical properties. This salt formation occurs when the chloride ion (Cl-) from hydrochloric acid bonds with the positively charged berberine molecule.
Structural differences affecting bioavailability
The structural differences between berberine and berberine HCl play a crucial role in their bioavailability. Bioavailability refers to the extent and rate at which a substance is absorbed and becomes available at the site of physiological activity.
Berberine HCl's salt form enhances its solubility in water, which is a key factor in improving its absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. The increased solubility allows for better dissolution in the intestinal fluids, leading to improved uptake by the body. This enhanced bioavailability means that a lower dose of berberine HCl may be required to achieve the same therapeutic effects as a higher dose of pure berberine.
Impact of HCl salt on berberine's chemical properties
The addition of hydrochloride to berberine not only affects its bioavailability but also influences other chemical properties. Berberine HCl typically exhibits greater stability, especially in acidic environments like the stomach. This stability can lead to a more consistent release and absorption of the compound throughout the digestive process.
Moreover, the salt form can impact the compound's melting point, solubility profile, and even its interaction with other molecules in the body. These modifications in chemical properties can influence how berberine HCl behaves in various formulations and how it interacts with biological systems, potentially affecting its overall efficacy and applications in health supplements and research.


Solubility and Stability Compared
Water solubility: Berberine HCl vs pure berberine
The water solubility of berberine HCl significantly surpasses that of pure berberine. This enhanced solubility is a crucial factor in the compound's effectiveness as a dietary supplement. Pure berberine, being less soluble in water, may not dissolve as readily in the gastrointestinal fluids, potentially limiting its absorption.
Berberine HCl's superior water solubility stems from its salt form. The chloride ion in berberine HCl helps to break the strong intermolecular forces present in pure berberine, allowing water molecules to surround and dissolve the compound more easily. This increased solubility translates to improved dissolution rates in the body, which can lead to more efficient absorption and potentially greater biological activity.
Stability in different pH environments
Their stability can vary significantly across different pH environments. This aspect is particularly important when considering the compound's journey through the human digestive system, which exposes it to a range of pH levels.
Berberine HCl generally demonstrates superior stability in acidic conditions, such as those found in the stomach. This stability allows it to withstand the harsh gastric environment without significant degradation. As the compound moves into the more alkaline environment of the intestines, it maintains a degree of stability that supports its absorption.
Pure berberine, while still relatively stable, may be more susceptible to pH-induced changes. These variations in stability across different pH levels can affect the compound's bioavailability and overall effectiveness in the body.
Shelf life and storage considerations for both forms
The shelf life and storage requirements of berberine and berberine HCl are important considerations for manufacturers, retailers, and consumers. Generally, berberine HCl exhibits a longer shelf life compared to pure berberine. This extended stability is partly due to its salt form, which provides some protection against environmental factors that can degrade the compound.
Both forms should be stored in cool, dry places away from direct sunlight to maintain their potency. However, berberine HCl may be less sensitive to humidity and temperature fluctuations, making it somewhat easier to store and transport. This enhanced stability can be particularly beneficial for supplement manufacturers, as it allows for longer product shelf lives and potentially reduces the need for special storage conditions.

Efficacy in Different Body Systems
Absorption rates in the gastrointestinal tract
The absorption rates of berberine and berberine HCl in the gastrointestinal tract differ significantly, largely due to their varying solubility profiles. Berberine HCl, with its enhanced water solubility, is generally absorbed more efficiently in the intestines. This improved absorption can lead to higher bioavailability, meaning more of the active compound reaches the bloodstream and target tissues.
Studies have shown that the absorption of pure berberine is relatively low, with estimates suggesting that only about 5% of an oral dose is absorbed. In contrast, berberine HCl's absorption rate is notably higher, although exact figures can vary depending on the specific formulation and individual factors. This increased absorption efficiency is one of the primary reasons why berberine HCl is often preferred in dietary supplements.
Berberine vs Berberine HCl for blood sugar control
Both have shown potential in supporting healthy blood sugar levels, but their efficacy can differ due to their absorption rates. Berberine HCl, with its superior bioavailability, may offer more consistent and potent effects on blood glucose regulation.
Research suggests that berberine compounds can influence blood sugar levels through various mechanisms, including enhancing insulin sensitivity and promoting glucose uptake in cells. The improved absorption of berberine HCl may allow for these effects to be achieved at lower doses compared to pure berberine, potentially offering more efficient support for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
Comparative effects on cardiovascular health
Their impact on cardiovascular health has been a subject of increasing interest in recent years. Both forms have shown potential benefits, but the enhanced bioavailability of berberine HCl may translate to more pronounced effects.
Studies have indicated that berberine compounds can support healthy lipid profiles and promote overall cardiovascular wellness. The improved absorption of berberine HCl may allow for these benefits to be realized more effectively, potentially offering stronger support for heart health at lower doses compared to pure berberine.
While berberine and berberine HCl share the same core compound, their differences in chemical structure, solubility, and bioavailability lead to distinct characteristics and potential benefits. Berberine HCl's enhanced solubility and absorption make it a preferred choice in many dietary supplements and research studies. Its improved stability and potentially greater efficacy in supporting various aspects of health, including blood sugar regulation and cardiovascular wellness, highlight its advantages over pure berberine.
Berberine HCL Powder Supplier
Shaanxi Rebeccia is a leading berberine hcl powder supplier in China, committed to delivering high-quality products for the health supplement industry. Our production base is equipped with internationally leading extraction, separation, and purification equipment, and operates in strict compliance with GMP and ISO standards. From raw material procurement to finished product delivery, every step undergoes rigorous quality control to ensure the safety and efficacy of our products. Our product specification is 97%. For inquiries about our product, contact us at information@sxrebecca.com.
References
- Zhang, Y., et al. (2020). Berberine: A Review of Its Pharmacological Properties and Therapeutic Potential in Metabolic Disorders. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 63(15), 8388-8407.
- Chen, W., et al. (2019). Comparative Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability of Berberine and Berberine Hydrochloride in Healthy Subjects. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 566, 71-76.
- Neag, M. A., et al. (2018). Berberine: Botanical Occurrence, Traditional Uses, Extraction Methods, and Relevance in Cardiovascular, Metabolic, Hepatic, and Renal Disorders. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 9, 557.
- Pirillo, A., & Catapano, A. L. (2015). Berberine, a Plant Alkaloid with Lipid- and Glucose-Lowering Properties: From in vitro Evidence to Clinical Studies. Atherosclerosis, 243(2), 449-461.
- Cicero, A. F., & Baggioni, A. (2016). Berberine and Its Role in Chronic Disease. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 928, 27-45.








