Compare UV–Vis and HPLC for quantifying curcumin solubility
When it comes to analyzing curcumin extract powder, two powerful analytical techniques stand out: UV-Vis spectroscopy and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). Both methods offer unique advantages for quantifying curcumin solubility, a critical factor in assessing the quality and efficacy of curcumin-based products. UV-Vis provides rapid screening capabilities, while HPLC excels in detailed compound separation and identification. This comparison explores the strengths and limitations of each technique, helping researchers and quality control professionals make informed decisions when working with curcumin extracts.

【English name】: Curcumin
【Latin Name】: Curcuma longa L.
【CAS No.】: 458-37-7
【Molecular Formula】: C21H20O6
【Active ingredients】: Curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin.
【Specification】: 10%~ 95% CP/EP/USP
【Use Part】 : Subterranean rhizome
【Appearance】: Orange yellow powder
【Mesh size】:80 Mesh
【Test Method】: HPLC
Specificity and Sensitivity
HPLC's superior selectivity for curcumin analysis
HPLC demonstrates unparalleled selectivity in curcumin analysis, making it the gold standard for precise quantification of curcuminoids in complex matrices. This chromatographic technique separates individual compounds based on their interactions with the stationary and mobile phases, allowing for the identification and measurement of specific curcuminoids – curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxycurcumin – with remarkable accuracy.
The power of HPLC lies in its ability to resolve structurally similar compounds, which is particularly valuable when analyzing curcumin extract powder. By employing various column types and optimizing mobile phase compositions, HPLC can achieve baseline separation of curcuminoids, even in the presence of other plant metabolites or potential interfering substances. This level of specificity ensures that the quantification of curcumin solubility is not compromised by the presence of related compounds or matrix effects.
UV-Vis detection limits for curcumin quantification
While UV-Vis spectroscopy may not match HPLC's selectivity, it offers impressive sensitivity for curcumin quantification. The distinctive absorption spectrum of curcumin, with a maximum around 420-430 nm, allows for sensitive detection even at low concentrations. Modern UV-Vis instruments can achieve detection limits in the nanogram range, making them suitable for many routine analyses of curcumin extract powder.
However, it's important to note that UV-Vis measurements can be influenced by the presence of other compounds absorbing in the same wavelength range. This limitation becomes more pronounced when dealing with complex herbal extracts or formulations containing multiple active ingredients. In such cases, the specificity of HPLC often proves advantageous for accurate curcumin quantification.
Comparing accuracy in complex extract matrices
When analyzing curcumin solubility in complex extract matrices, the choice between UV-Vis and HPLC becomes crucial. HPLC's ability to separate individual components before detection provides a significant advantage in accuracy. This separation minimizes the risk of overestimation due to spectral overlap or matrix interferences, which can be a concern with UV-Vis measurements.
In contrast, UV-Vis spectroscopy relies on the total absorbance at a specific wavelength, which can lead to potential inaccuracies in complex samples. While this may be sufficient for rapid screening or quality control of relatively pure curcumin extracts, it may fall short when dealing with more complex formulations or when precise quantification of individual curcuminoids is required.
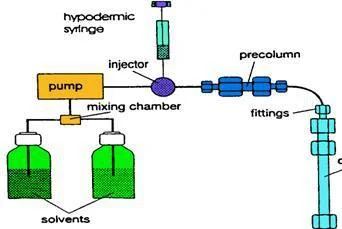

Sample Preparation
Extraction methods for curcumin powder samples
Effective sample preparation is crucial for accurate curcumin analysis, regardless of the chosen analytical method. For curcumin extract powder, common extraction techniques include solvent extraction, ultrasound-assisted extraction, and microwave-assisted extraction. The choice of extraction method can significantly impact the solubility and recovery of curcuminoids, ultimately affecting the quantification results.
Solvent extraction remains a popular choice due to its simplicity and effectiveness. Ethanol, methanol, and acetone are commonly used solvents, each offering different extraction efficiencies. Ultrasound-assisted extraction can enhance the extraction process by improving solvent penetration and mass transfer, potentially leading to higher yields of curcuminoids. Microwave-assisted extraction offers rapid extraction times but requires careful optimization to avoid thermal degradation of curcumin.
Solvent selection impacts on UV-Vis vs HPLC results
The choice of solvent plays a critical role in both UV-Vis and HPLC analyses of curcumin extract powder. For UV-Vis spectroscopy, the solvent can affect the absorption spectrum of curcumin, potentially shifting the wavelength of maximum absorption or altering the molar absorptivity. This impact is particularly important when developing calibration curves and comparing results across different studies.
In HPLC analysis, solvent selection influences both the extraction efficiency and the chromatographic separation. The solvent must be compatible with the mobile phase to avoid peak distortion or changes in retention time. Additionally, the solubility of curcumin in the chosen solvent directly affects the sample concentration and, consequently, the sensitivity of the analysis.
Sample clean-up techniques for improved analysis
Sample clean-up is often necessary to remove interfering compounds and improve the accuracy of curcumin quantification. For UV-Vis analysis, simple filtration or centrifugation may be sufficient to remove particulates. However, more complex samples may require additional steps such as liquid-liquid extraction or solid-phase extraction to isolate curcuminoids from other matrix components.
HPLC analysis typically benefits from more rigorous sample clean-up procedures. Solid-phase extraction cartridges can be used to selectively retain curcuminoids while washing away potential interferents. This step not only improves the accuracy of quantification but also prolongs the life of HPLC columns by reducing the introduction of matrix contaminants.

Analysis Time and Complexity
Rapid UV-Vis screening of curcumin content
UV-Vis spectroscopy excels in providing rapid screening of curcumin content in extract powders. The simplicity of the technique allows for quick sample preparation and almost instantaneous measurements. Modern UV-Vis spectrometers can complete a full spectrum scan in seconds, making it possible to analyze multiple samples in a short time frame.
This speed makes UV-Vis an attractive option for high-throughput quality control processes in the production of curcumin-based supplements or functional foods. It allows manufacturers to quickly assess the curcumin content of raw materials or finished products, ensuring consistency across batches. However, the trade-off for this rapidity is the potential loss of specificity, especially in complex matrices.
HPLC run times for thorough curcuminoid separation
HPLC analysis of curcuminoids typically requires longer run times compared to UV-Vis measurements. A standard HPLC method for curcumin analysis might take 10-30 minutes per sample, depending on the complexity of the extract and the desired level of separation. This longer analysis time is a result of the chromatographic separation process, where individual compounds are resolved as they travel through the column.
While the extended run time may seem disadvantageous, it's important to consider the wealth of information provided by HPLC analysis. Not only does it quantify total curcumin content, but it also separates and quantifies individual curcuminoids, providing a more comprehensive profile of the extract. This detailed analysis is particularly valuable for research applications and stringent quality control requirements.
Cost-effectiveness: UV-Vis vs HPLC for routine QC
When considering cost-effectiveness for routine quality control of curcumin extract powder, both UV-Vis and HPLC have their merits. UV-Vis spectrophotometers are generally less expensive to purchase and maintain compared to HPLC systems. They also require less specialized training to operate, potentially reducing labor costs.
HPLC, while more expensive in terms of initial investment and ongoing maintenance, offers superior specificity and accuracy. For companies producing high-value curcumin products or those requiring detailed compositional analysis, the additional cost of HPLC may be justified by the quality of data obtained. Moreover, the ability to analyze multiple compounds in a single run can make HPLC more cost-effective in the long term for comprehensive quality control programs.
In the analysis of curcumin extract powder, both UV-Vis spectroscopy and HPLC offer valuable insights into curcumin solubility and content. UV-Vis provides rapid, cost-effective screening suitable for routine quality control, while HPLC excels in detailed compositional analysis and accuracy in complex matrices. The choice between these techniques depends on specific analytical needs, sample complexity, and regulatory requirements. For comprehensive characterization of curcumin extracts, a combination of both methods may offer the most robust analytical approach, ensuring both efficiency and precision in quality control and research applications.

China Curcumin Extract Powder Supplier
Shaanxi Rebeccia stands at the forefront of curcumin powder production, leveraging cutting-edge extraction and purification technologies to deliver premium-quality products. Our state-of-the-art facilities operate under strict GMP and ISO standards, ensuring unparalleled consistency and purity in every batch. We offer curcumin with specifications ranging from 10% to 95% CP/EP/USP, catering to the diverse needs of various industries. Our products, derived from the subterranean rhizome of Curcuma longa, undergo rigorous quality control at every stage of production. The vibrant orange-yellow powder, with a standardized 80 mesh size, is ideal for various applications in the pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and cosmetic industries. For inquiries about our high-quality curcumin extract powder or to discuss your specific requirements, contact us at information@sxrebecca.com. Experience the difference that precision, purity, and professionalism can make in your curcumin-based products.
References
- Jayaprakasha, G. K., Rao, L. J., & Sakariah, K. K. (2002). Improved HPLC method for the determination of curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxycurcumin. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 50(13), 3668-3672.
- Priyadarsini, K. I. (2014). The chemistry of curcumin: from extraction to therapeutic agent. Molecules, 19(12), 20091-20112.
- Pabon, H. J. J. (1964). A synthesis of curcumin and related compounds. Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas, 83(4), 379-386.
- Tonnesen, H. H., & Karlsen, J. (1985). Studies on curcumin and curcuminoids. VI. Kinetics of curcumin degradation in aqueous solution. Zeitschrift für Lebensmittel-Untersuchung und Forschung, 180(5), 402-404.
- Lee, W. H., Loo, C. Y., Bebawy, M., Luk, F., Mason, R. S., & Rohanizadeh, R. (2013). Curcumin and its derivatives: their application in neuropharmacology and neuroscience in the 21st century. Current Neuropharmacology, 11(4), 338-378.
- Anand, P., Kunnumakkara, A. B., Newman, R. A., & Aggarwal, B. B. (2007). Bioavailability of curcumin: problems and promises. Molecular Pharmaceutics, 4(6), 807-818.








