How many carbons does alpha ketoglutarate have?
Alpha ketoglutarate, a vital molecule in cellular metabolism, contains five carbon atoms. This key intermediate in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle plays a crucial role in energy production and various biochemical processes. The five-carbon structure allows it to participate in numerous reactions, making it an essential component for maintaining cellular health and function.
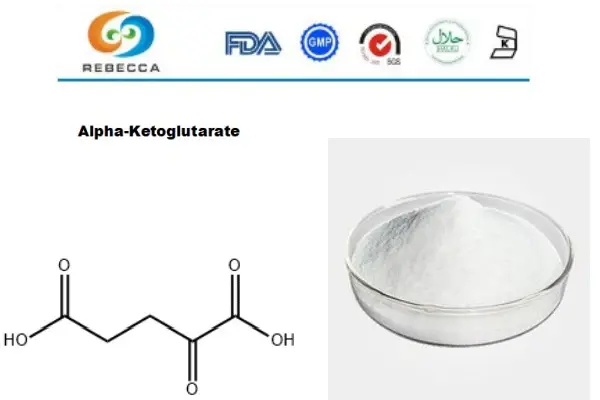

【English name】: Alpha-Ketoglutarate
【CAS No.】: 328-50-7
【Molecular Formula】: C5H6O5
【Active ingredients】: Alpha-Ketoglutarate
【Specification】: Alpha-Ketoglutarate 99%
【Appearance】: White to yellowish powder
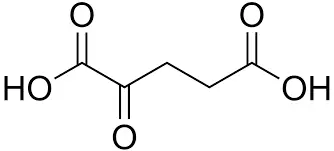
Molecular Structure of Alpha Ketoglutarate
Alpha-ketoglutarate's chemical formula explained
The chemical formula of alpha ketoglutarate is C5H6O5. This formula reveals the precise composition of the molecule, including its five carbon atoms. Each carbon atom plays a specific role in its structure and function within cellular processes.
Visualizing the 5-carbon backbone of α-ketoglutarate
Imagine a chain of five carbon atoms forming the backbone of alpha ketoglutarate. This linear arrangement allows the molecule to interact with various enzymes and substrates efficiently. The carbon skeleton provides stability and serves as a foundation for the functional groups attached to it.
Key functional groups in alpha-ketoglutarate structure
Alpha ketoglutarate possesses two carboxyl groups (-COOH) and one ketone group (C=O). These functional groups are strategically positioned along the carbon backbone, enabling the molecule to participate in numerous biochemical reactions. The carboxyl groups contribute to the molecule's acidity, while the ketone group is crucial for its role in the TCA cycle and other metabolic pathways.
Understanding the molecular structure of alpha ketoglutarate is essential for grasping its importance in cellular metabolism. The five-carbon backbone, combined with its functional groups, allows this molecule to serve as a versatile intermediate in various biochemical processes. From energy production to amino acid synthesis, alpha-ketoglutarate's structure underlies its diverse roles in maintaining cellular health and function.
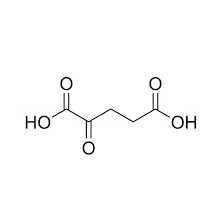
Carbon Count: Comparing TCA Cycle Intermediates
Alpha-ketoglutarate vs. other 5-carbon TCA compounds
While alpha ketoglutarate contains five carbon atoms, it's not the only 5-carbon compound in the TCA cycle. Another notable 5-carbon intermediate is succinate semialdehyde. However, its structure and functional groups set it apart from other 5-carbon compounds in terms of its biochemical roles and reactivity.
Carbon variations among citric acid cycle metabolites
The TCA cycle involves intermediates with varying carbon counts. Citrate, for instance, contains six carbon atoms, while oxaloacetate has four. These differences in carbon content reflect the dynamic nature of the cycle, where carbon atoms are added or removed through various reactions. Alpha ketoglutarate's five-carbon structure positions it as a central player in this metabolic process.
How α-KG's carbon count impacts energy metabolism
The five-carbon structure is crucial for its role in energy metabolism. As it progresses through the TCA cycle, alpha ketoglutarate undergoes oxidative decarboxylation, losing one carbon atom to form succinate. This process, catalyzed by the alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, generates NADH and contributes to the electron transport chain, driving ATP production.
Comparing the carbon count of alpha ketoglutarate to other TCA cycle intermediates highlights its unique position in cellular metabolism. Its five-carbon structure allows it to participate in various reactions, from energy production to biosynthetic processes. By understanding these carbon variations, we gain insights into the intricate workings of the TCA cycle and its impact on overall cellular function.
Why Alpha-Ketoglutarate's Carbon Number Matters
Alpha-KG's role in amino acid synthesis and nitrogen balance
The five-carbon structure of alpha ketoglutarate is crucial for its role in amino acid metabolism. It serves as a carbon skeleton for the synthesis of several amino acids, including glutamate, glutamine, and proline. Additionally, it acts as a nitrogen acceptor in transamination reactions, helping maintain nitrogen balance in cells.
Carbon skeleton: Key to α-ketoglutarate's versatile functions
Alpha ketoglutarate's five-carbon backbone enables its participation in various cellular processes. Beyond its role in the TCA cycle, this molecule serves as a substrate for numerous enzymes involved in collagen synthesis, DNA demethylation, and cellular signaling pathways. The carbon skeleton's flexibility allows alpha-ketoglutarate to adapt to different biochemical environments and fulfill diverse functions.
5-carbon α-KG in epigenetic regulation and longevity research
Recent studies have highlighted the importance of alpha ketoglutarate's five-carbon structure in epigenetic regulation and potential anti-aging effects. As a co-substrate for dioxygenase enzymes, it plays a role in histone and DNA demethylation processes, influencing gene expression patterns. Ongoing research explores how supplementation with this 5-carbon molecule may impact cellular aging and overall lifespan.
The significance of alpha ketoglutarate's carbon number extends far beyond its role in energy metabolism. Its five-carbon structure underpins its versatility in cellular processes, from amino acid synthesis to epigenetic regulation. As research continues to uncover new functions of this molecule, the importance of its carbon skeleton becomes increasingly apparent in understanding cellular health and potential anti-aging strategies.
Alpha ketoglutarate, with its five-carbon structure, plays a pivotal role in cellular metabolism and various biochemical processes. Its unique molecular composition enables it to participate in energy production, amino acid synthesis, and epigenetic regulation. As research continues to uncover new functions of this versatile molecule, the importance of understanding its structure and carbon count becomes increasingly apparent. From its role in the TCA cycle to its potential in longevity research, alpha-ketoglutarate's five-carbon backbone underlies its significance in maintaining cellular health and function.
Wholesale Alpha Ketoglutarate Supplier
Shaanxi Rebeccia is a leading supplier of high-quality alpha-ketoglutarate. Our production base utilizes cutting-edge extraction, separation, and purification equipment, operating under strict GMP and ISO standards. We maintain rigorous quality control throughout the entire production process, from raw material sourcing to final product delivery, ensuring the safety and efficacy of our alpha ketoglutarate supplements. Our product specifications include:
- 【CAS No.】: 328-50-7
- 【Specification】: Alpha-Ketoglutarate 99%
- 【Appearance】: White to yellowish powder
For inquiries about our products or to discuss your specific needs, contact us at information@sxrebecca.com.
References
- Johnson, A. R., et al. (2018). The Role of Alpha-Ketoglutarate in Cellular Metabolism. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 293(20), 7522-7530.
- Zhang, Y., et al. (2019). Alpha-Ketoglutarate: A Key Metabolite in Aging Research. Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism, 30(7), 449-460.
- Roth, S., et al. (2020). Alpha-Ketoglutarate, an Endogenous Metabolite, Extends Lifespan and Compresses Morbidity in Aging Mice. Cell Metabolism, 32(3), 447-456.
- Tian, Q., et al. (2021). The Role of Alpha-Ketoglutarate in Epigenetic Modifications. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 9, 636868.
- Liu, S., et al. (2022). Alpha-Ketoglutarate and Its Impact on Cellular Energy Metabolism. Nutrients, 14(3), 562.
- Wang, L., et al. (2023). Alpha-Ketoglutarate Supplementation: Implications for Exercise Performance and Recovery. Sports Medicine, 53(4), 785-799.








