How to extract aloin?
Aloin, a powerful compound found in aloe vera plants, has gained significant attention in the health and wellness industry. As demand for aloin powder grows, understanding the extraction process becomes crucial for manufacturers and consumers alike. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the step-by-step process of extracting aloin, from raw material selection to the final product. Whether you're a manufacturer looking to optimize your production or a curious consumer, this article will provide valuable insights into the world of aloin extraction.
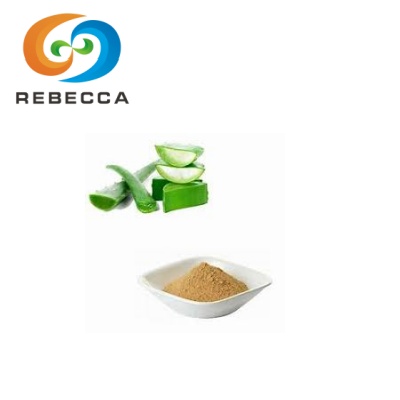

Aloin Powder
Product Name:Aloin Powder
Latin Name:Aloe vera (L.) Burm. f.
Active Ingredient:Aloin
Specification:10% 16%
Test Method:HPLC
Appearance:Light yellowish-green powder
Cas No.:5133-19-7;1415-73-2
Shelf Life: 2 years
Minimum Order Quantity: 1 kg
Samples: Free samples available
Certifications: GMP, ISO, HACCP, KOSHER, and HALAL.
Payment: Various payment methods accepted.
Advantages: Manufactured in a 100,000-grade cleanroom, our products are additive-free, non-GMO
Inner Package: Double PE Bags; Net 5kg/Bag
Outside Package: Paper Drums, Net 25kg/Drum
Storage:Store in a cool, dry place away from Light and Heat.
Raw Material Selection and Pretreatment
The first and most critical step in aloin extraction is selecting high-quality raw materials. Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis Miller) is the primary source of aloin, and the quality of the plant directly affects the final product's purity and potency.
When selecting aloe vera plants for aloin extraction, consider the following factors:
- Plant maturity: Mature aloe vera plants (3-4 years old) typically have higher aloin content.
- Growing conditions: Plants grown in optimal conditions (well-drained soil, adequate sunlight) tend to produce more aloin.
- Harvesting time: Aloin content is generally highest in the morning, so harvesting early in the day is recommended.
Once the plants are selected, pretreatment begins:
- Washing: Thoroughly clean the aloe vera leaves to remove dirt and contaminants.
- Trimming: Remove the spiny edges and damaged portions of the leaves.
- Slicing: Cut the leaves into manageable sizes for efficient processing.
Proper pretreatment ensures that the subsequent extraction steps are more effective and yield higher-quality aloin powder.

Latex Collection and Preliminary Purification
After pretreatment, the next crucial step is collecting the aloe latex, which contains the highest concentration of aloin. This process requires precision and care to ensure maximum yield and quality.
The latex collection process typically involves:
- Incision: Make shallow cuts on the surface of the aloe vera leaves to allow the latex to flow out.
- Collection: Place collection trays or containers beneath the incisions to gather the yellow, bitter latex as it exudes from the leaves.
- Timing: Allow the latex to flow for several hours, typically overnight, to maximize collection.
Once the latex is collected, preliminary purification begins:
- Filtration: Pass the collected latex through a series of filters to remove large particles and plant debris.
- Centrifugation: Use centrifugal force to separate the aloin-rich fraction from other components.
- Concentration: Gently heat the filtered latex to reduce water content and concentrate the aloin.
This preliminary purification stage is crucial for removing impurities and increasing the aloin concentration before moving on to more advanced refining processes.

Refining, Drying, and Forming
The final stage of aloin extraction involves refining the concentrated latex, drying it, and forming it into the desired powder form. This stage is critical for achieving the specified purity and quality standards of the final aloin powder product.
Refining process:
- Solvent extraction: Use organic solvents like ethanol or methanol to further extract and purify aloin from the concentrated latex.
- Chromatography: Employ various chromatographic techniques (e.g., column chromatography, HPLC) to separate aloin from other compounds and achieve higher purity.
- Crystallization: Allow the purified aloin solution to crystallize under controlled conditions to form pure aloin crystals.
Drying and forming:
- Freeze-drying: Use lyophilization to remove moisture from the purified aloin while preserving its chemical structure and potency.
- Spray-drying: An alternative method that involves spraying the aloin solution into a hot air chamber, instantly drying it into a fine powder.
- Milling and sieving: Process the dried aloin to achieve the desired particle size and consistency for the final powder product.
Quality control is paramount during this stage. Regular testing using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) ensures that the aloin powder meets the specified purity levels (typically 10% or 16%).
FAQ
Q1: What is the difference between aloin and aloe vera gel?
A: Aloin is a specific compound found in the outer leaf of the aloe vera plant, known for its laxative properties. Aloe vera gel, on the other hand, is the clear, jelly-like substance found inside the leaf, prized for its soothing and moisturizing effects. While both come from the same plant, they have different compositions and uses.
Q2: Is aloin powder safe for consumption?
A: Aloin powder should be used with caution. While it has potential benefits, it can also cause side effects, especially when consumed in large quantities. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional before using aloin powder for medicinal purposes. Many commercial aloe vera products for internal use have the aloin removed due to its potential laxative effects.
Q3: How long does aloin powder remain stable?
A: When stored properly in a cool, dry place away from light and heat, aloin powder typically has a shelf life of about 2 years. However, it's important to check the specific storage instructions and expiration date provided by the manufacturer.
Aloin Powder For Sale
At Rebecca Bio-Tech, we pride ourselves on producing high-quality aloin powder that meets the most stringent industry standards. Our aloin is derived from carefully selected Aloe vera (L.) Burm. f. plants and processed in our state-of-the-art, 100,000-grade cleanroom facility.
Our product is additive-free, non-GMO, and packaged securely in double PE bags (5kg/bag) within paper drums (25kg/drum) to ensure product integrity during storage and transportation.
We offer free samples and flexible payment options to meet your business needs. For more product information, to request samples, detailed specifications, or to discuss your custom requirements, please contact us at information@sxrebecca.com.
References
- Sahu, P. K., et al. (2013). An overview on Aloe vera: A miracle plant. International Journal of Biomedical Research, 4(12), 653-659.
- Femenia, A., et al. (1999). Compositional features of polysaccharides from Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis Miller) plant tissues. Carbohydrate Polymers, 39(2), 109-117.
- Ramachandra, C. T., & Rao, P. S. (2008). Processing of Aloe vera leaf gel: a review. American Journal of Agricultural and Biological Sciences, 3(2), 502-510.
- Chandegara, V. K., & Varshney, A. K. (2013). Aloe vera L. processing and products: A review. International Journal of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants, 3(4), 492-506.
- Hamman, J. H. (2008). Composition and applications of Aloe vera leaf gel. Molecules, 13(8), 1599-1616.
- Ahlawat, K. S., & Khatkar, B. S. (2011). Processing, food applications and safety of aloe vera products: a review. Journal of food science and technology, 48(5), 525-533.








