Tetrahydrocurcumin VS Hydroquinone
In the ever-evolving world of skincare, the quest for effective skin lightening agents continues to captivate both consumers and researchers alike. Two compounds that have gained significant attention in this arena are tetrahydrocurcumin">tetrahydrocurcumin and hydroquinone. This article delves into a detailed comparison of these two substances, exploring their sources, chemical nature, mechanisms of action, and regulatory status.
Tetrahydrocurcumin
【English name】: Tetrahydrocurcumin
【CAS No.】: 36062-04-1
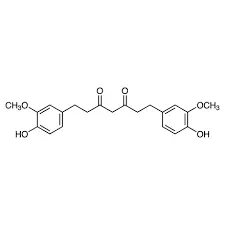
【Molecular Formula】:C21H24O6
【Active ingredients】: Tetrahydrocurcumin
【Specification】: Tetrahydrocurcumin 98%
【Appearance】: white powder
Source and Chemical Nature
They are two distinct compounds with different origins and chemical structures, each offering unique properties for skin lightening applications.
Tetrahydrocurcumin (THC) is a bioactive metabolite of curcumin, the primary active compound found in turmeric (Curcuma longa). It is a naturally occurring substance that results from the reduction of curcumin in the body. Chemically, it has the molecular formula C21H24O6 and a CAS number of 36062-04-1. It appears as a white powder and is known for its potent antioxidant properties.
On the other hand, hydroquinone is a synthetic compound with the chemical formula C6H6O2. It is produced industrially and has been widely used in skincare products for its skin-lightening effects. Hydroquinone is a type of phenol, structurally consisting of a benzene ring with two hydroxyl groups in the para position.
The natural origin of tetrahydrocurcumin contrasts sharply with the synthetic nature of hydroquinone, which has implications for their perceived safety and regulatory status. This fundamental difference in source and chemical nature sets the stage for their divergent approaches to skin lightening.
Mechanism of Action: Different Pathways to Lighten Skin
While both of them are used for skin lightening, they achieve this effect through distinct mechanisms of action.
Tetrahydrocurcumin works primarily as a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent. Its skin-lightening properties are attributed to its ability to inhibit tyrosinase, the key enzyme in melanin production. By reducing tyrosinase activity, tetrahydrocurcumin effectively decreases melanin synthesis, leading to a lighter skin tone. Additionally, its antioxidant properties help protect the skin from free radical damage, which can contribute to hyperpigmentation.
Hydroquinone, in contrast, acts as a melanin synthesis inhibitor through a more direct and potent mechanism. It works by interfering with the function of melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin. Hydroquinone inhibits the enzyme tyrosinase and may also damage melanocytes, leading to a significant reduction in melanin production. This strong inhibitory effect is what makes hydroquinone highly effective but also potentially more risky in terms of side effects.
The gentler approach of tetrahydrocurcumin, which focuses on antioxidant protection alongside melanin inhibition, contrasts with the more aggressive melanin-suppressing action of hydroquinone. This difference in mechanism contributes to their varying efficacy and safety profiles, influencing their use and regulation in skincare products.
Regulatory Status and Safety Considerations
The regulatory landscape reflects their different origins, mechanisms of action, and safety profiles.
Tetrahydrocurcumin, being a natural derivative of curcumin, generally faces fewer regulatory restrictions. It is considered a safe ingredient in many countries and is widely used in cosmetic and nutraceutical products. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not issued specific regulations for tetrahydrocurcumin, but it is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) when used in food applications. In skincare, it is often marketed as a natural and gentle alternative to more aggressive skin-lightening agents.
Hydroquinone, on the other hand, has a more complex regulatory status due to safety concerns. In the United States, over-the-counter products containing hydroquinone are limited to a 2% concentration, while higher concentrations require a prescription. The European Union has banned hydroquinone in cosmetic products due to potential health risks, including possible carcinogenicity and ochronosis (a blue-black discoloration of the skin). Many other countries have also imposed restrictions or bans on hydroquinone use in cosmetics.
The safety profile of tetrahydrocurcumin is generally considered more favorable than that of hydroquinone. Tetrahydrocurcumin has not been associated with the same level of side effects or long-term risks as hydroquinone. This difference in safety considerations has led to a growing preference for tetrahydrocurcumin and other natural alternatives in the skincare industry, particularly for long-term use or in products intended for sensitive skin.
FAQ
Q1: Is tetrahydrocurcumin as effective as hydroquinone for skin lightening?
A: While hydroquinone is known for its potent and rapid skin-lightening effects, tetrahydrocurcumin offers a gentler approach with fewer side effects. Tetrahydrocurcumin may take longer to show visible results, but it is considered safer for long-term use. Its effectiveness can vary depending on individual skin types and the specific formulation used.
Q2: Can tetrahydrocurcumin be used safely on all skin types?
A: Tetrahydrocurcumin is generally considered safe for all skin types, including sensitive skin. Its natural origin and antioxidant properties make it less likely to cause irritation compared to hydroquinone. However, as with any skincare product, it's advisable to perform a patch test before regular use and consult with a dermatologist, especially if you have specific skin concerns.
Tetrahydrocurcumin For Sale
Tetrahydrocurcumin stands out as a compelling alternative to conventional skin-lightening ingredients such as hydroquinone. Derived from natural sources, this compound combines efficacy with a gentle profile, making it ideal for individuals seeking safer, well-tolerated solutions for hyperpigmentation and uneven skin tone. Its mechanism is supported by strong antioxidant activity, which not only helps reduce melanin production but also protects the skin from oxidative stress, contributing to overall skin health and brightness.
Unlike harsher agents that may cause irritation or long-term side effects, this ingredient offers a favorable safety record, making it suitable for prolonged use across various skin types. As scientific interest grows, emerging studies continue to validate its role in cosmetic formulations, reinforcing its potential to become a staple in modern skincare development.
At Rebecca Bio-Tech, we provide a premium-grade version of this active with rigorous quality control.
CAS No.: 36062-04-1
Molecular Formula: C₂₁H₂₄O₆
Active Ingredient: Tetrahydrocurcumin
Purity: 98%
Appearance: White powder
We welcome inquiries for samples, technical data sheets, or discussions on tailored solutions for your product line. For assistance, please reach out to us at information@sxrebecca.com. Our specialists are available to support your formulation needs with reliable, high-performance ingredients.
References
[1] Panahi, Y., Khalili, N., Sahebi, E., Namazi, S., Karimian, M. S., Majeed, M., & Sahebkar, A. (2017). Antioxidant effects of curcuminoids in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. Complementary Therapies in Medicine, 33, 1-5.
[2] Solano, F., Briganti, S., Picardo, M., & Ghanem, G. (2006). Hypopigmenting agents: an updated review on biological, chemical and clinical aspects. Pigment Cell Research, 19(6), 550-571.
[3] Draelos, Z. D. (2007). Skin lightening preparations and the hydroquinone controversy. Dermatologic Therapy, 20(5), 308-313.





 EXTRACT_1756803389333.jpg)


